CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs
- PMID: 26669964
- PMCID: PMC4829301
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1128065
CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs
Abstract
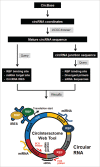
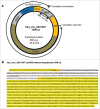
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are widely expressed in animal cells, but their biogenesis and functions are poorly understood. CircRNAs have been shown to act as sponges for miRNAs and may also potentially sponge RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and are thus predicted to function as robust posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression. The joint analysis of large-scale transcriptome data coupled with computational analyses represents a powerful approach to elucidate possible biological roles of ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes. Here, we present a new web tool, CircInteractome (circRNA interactome), for mapping RBP- and miRNA-binding sites on human circRNAs. CircInteractome searches public circRNA, miRNA, and RBP databases to provide bioinformatic analyses of binding sites on circRNAs and additionally analyzes miRNA and RBP sites on junction and junction-flanking sequences. CircInteractome also allows the user the ability to (1) identify potential circRNAs which can act as RBP sponges, (2) design junction-spanning primers for specific detection of circRNAs of interest, (3) design siRNAs for circRNA silencing, and (4) identify potential internal ribosomal entry sites (IRES). In sum, the web tool CircInteractome, freely accessible at http://circinteractome.nia.nih.gov, facilitates the analysis of circRNAs and circRNP biology.
Keywords: CLIP-Seq; CircRNA-miRNA; RNA-binding proteins; circRNA IRES; circRNA siRNA; divergent primer design; sponge circRNAs; transcriptome.
Figures


References
-
- Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell type-specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet 2013; 9:e1003777; PMID:24039610; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M, et al.. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013; 495:333-8; PMID:23446348; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11928 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013; 19:141-57; PMID:23249747; http://dx.doi.org/10.1261/rna.035667.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One 2012; 7:e30733; PMID:22319583; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030733 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013; 495:384-8; PMID:23446346; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11993 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
