Attrition of Hepatic Damage Inflicted by Angiotensin II with α-Tocopherol and β-Carotene in Experimental Apolipoprotein E Knock-out Mice
- PMID: 26670291
- PMCID: PMC4680930
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18300
Attrition of Hepatic Damage Inflicted by Angiotensin II with α-Tocopherol and β-Carotene in Experimental Apolipoprotein E Knock-out Mice
Abstract
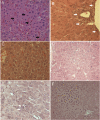
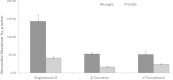
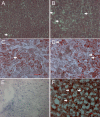
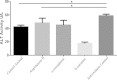
Angiotensin II is one of the key regulatory peptides implicated in the pathogenesis of liver disease. The mechanisms underlying the salubrious role of α-tocopherol and β-carotene on liver pathology have not been comprehensively assessed. Here, we investigated the mechanisms underlying the role of Angiotensin II on hepatic damage and if α-tocopherol and β-carotene supplementation attenuates hepatic damage. Hepatic damage was induced in Apoe(-/-)mice by infusion of Angiotensin II followed by oral administration with α-tocopherol and β-carotene-enriched diet for 60 days. Investigations showed fibrosis, kupffer cell hyperplasia, hepatocyte degeneration and hepatic cell apoptosis; sinusoidal dilatation along with haemorrhages; evidence of fluid accumulation; increased ROS level and increased AST and ALT activities. In addition, tPA and uPA were down-regulated due to 42-fold up-regulation of PAI-1. MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-12, and M-CSF were down-regulated in Angiotensin II-treated animals. Notably, α-tocopherol and β-carotene treatment controlled ROS, fibrosis, hepatocyte degeneration, kupffer cell hyperplasia, hepatocyte apoptosis, sinusoidal dilatation and fluid accumulation in the liver sinusoids, and liver enzyme levels. In addition, PAI-1, tPA and uPA expressions were markedly controlled by β-carotene treatment. Thus, Angiotensin II markedly influenced hepatic damage possibly by restraining fibrinolytic system. We concluded that α-tocopherol and β-carotene treatment has salubrious role in repairing hepatic pathology.
Figures





References
-
- Torok N. J. Recent advances in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol. 43, 315–321 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Hirose A. et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker inhibits fibrosis in rat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 45, 1375–1381 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Browatzki M. et al. Angiotensin II stimulates matrix metalloproteinase secretion in human vascular smooth muscle cells via nuclear factor- kappaB and activator protein 1 in a redox-sensitive manner. J Vasc Res. 42, 415–423 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Yoshiji H. & Fukui H. Renin-angiotensin system and progression of chronic liver diseases. J Gastroenterol. 41, 1020–1022 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

