Unbalanced recovery of regulatory and effector T cells after allogeneic stem cell transplantation contributes to chronic GVHD
- PMID: 26670634
- PMCID: PMC4742552
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-672345
Unbalanced recovery of regulatory and effector T cells after allogeneic stem cell transplantation contributes to chronic GVHD
Abstract
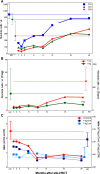
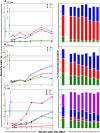
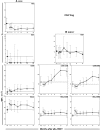
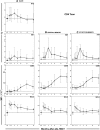
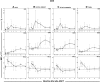
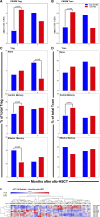
The development and maintenance of immune tolerance after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) requires the balanced reconstitution of donor-derived CD4 regulatory T cells (CD4Tregs) as well as effector CD4 (conventional CD4 T cells [CD4Tcons]) and CD8 T cells. To characterize the complex mechanisms that lead to unbalanced recovery of these distinct T-cell populations, we studied 107 adult patients who received T-replete stem cell grafts after reduced-intensity conditioning. Immune reconstitution of CD4Treg, CD4Tcon, and CD8 T cells was monitored for a 2-year period. CD3 T-cell counts gradually recovered to normal levels during this period but CD8 T cells recovered more rapidly than either CD4Tregs or CD4Tcons. Reconstituting CD4Tregs and CD4Tcons were predominantly central memory (CM) and effector memory (EM) cells and CD8 T cells were predominantly terminal EM cells. Thymic generation of naive CD4Tcon and CD8 T cells was maintained but thymic production of CD4Tregs was markedly decreased with little recovery during the 2-year study. T-cell proliferation was skewed in favor of CM and EM CD4Tcon and CD8 T cells, especially 6 to 12 months after HSCT. Intracellular expression of BCL2 was increased in CD4Tcon and CD8 T cells in the first 3 to 6 months after HSCT. Early recovery of naive and CM fractions within each T-cell population 3 months after transplant was also strongly correlated with the subsequent development of chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). These dynamic imbalances favor the production, expansion, and persistence of effector T cells over CD4Tregs and were associated with the development of chronic GVHD.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Seggewiss R, Einsele H. Immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation and expanding options for immunomodulation: an update. Blood. 2010;115(19):3861–3868. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, Sohn SK, Won DI, Lee NY, Suh JS, Lee KB. Rapid helper T-cell recovery above 200 x 10 6/l at 3 months correlates to successful transplant outcomes after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;37(12):1119–1128. - PubMed
-
- Storek J, Geddes M, Khan F, et al. Reconstitution of the immune system after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in humans. Semin Immunopathol. 2008;30(4):425–437. - PubMed
-
- Podgorny PJ, Liu Y, Dharmani-Khan P, et al. Immune cell subset counts associated with graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(4):450–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

