Enkephalin Disinhibits Mu Opioid Receptor-Rich Striatal Patches via Delta Opioid Receptors
- PMID: 26671460
- PMCID: PMC4698909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.010
Enkephalin Disinhibits Mu Opioid Receptor-Rich Striatal Patches via Delta Opioid Receptors
Abstract
Opioid neuropeptides and their receptors are evolutionarily conserved neuromodulatory systems that profoundly influence behavior. In dorsal striatum, which expresses the endogenous opioid enkephalin, patches (or striosomes) are limbic-associated subcompartments enriched in mu opioid receptors. The functional implications of opioid signaling in dorsal striatum and the circuit elements in patches regulated by enkephalin are unclear. Here, we examined how patch output is modulated by enkephalin and identified the underlying circuit mechanisms. We found that patches are relatively devoid of parvalbumin-expressing interneurons and exist as self-contained inhibitory microcircuits. Enkephalin suppresses inhibition onto striatal projection neurons selectively in patches, thereby disinhibiting their firing in response to cortical input. The majority of this neuromodulation is mediated by delta, not mu-opioid, receptors, acting specifically on intra-striatal collateral axons of striatopallidal neurons. These results suggest that enkephalin gates limbic information flow in dorsal striatum, acting via a patch-specific function for delta opioid receptors.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

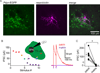
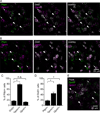

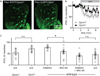



Comment in
-
Neuronal circuits: Patch work in the striatum.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Feb;17(2):75. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2015.23. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26697742 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993;264:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Besson MJ, Graybiel AM, Quinn B. Co-expression of neuropeptides in the cat’s striatum: an immunohistochemical study of substance P, dynorphin B and enkephalin. Neuroscience. 1990;39:33–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

