t(15;21) translocations leading to the concurrent downregulation of RUNX1 and its transcription factor partner genes SIN3A and TCF12 in myeloid disorders
- PMID: 26671595
- PMCID: PMC4681058
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0484-0
t(15;21) translocations leading to the concurrent downregulation of RUNX1 and its transcription factor partner genes SIN3A and TCF12 in myeloid disorders
Abstract
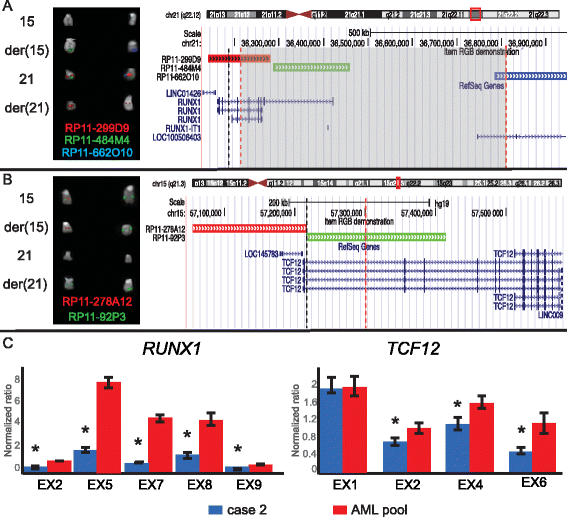
Through a combined approach integrating RNA-Seq, SNP-array, FISH and PCR techniques, we identified two novel t(15;21) translocations leading to the inactivation of RUNX1 and its partners SIN3A and TCF12. One is a complex t(15;21)(q24;q22), with both breakpoints mapped at the nucleotide level, joining RUNX1 to SIN3A and UBL7-AS1 in a patient with myelodysplasia. The other is a recurrent t(15;21)(q21;q22), juxtaposing RUNX1 and TCF12, with an opposite transcriptional orientation, in three myeloid leukemia cases. Since our transcriptome analysis indicated a significant number of differentially expressed genes associated with both translocations, we speculate an important pathogenetic role for these alterations involving RUNX1.
Figures

References
-
- Ingenuity Pathway Analysis IPA® QRC. http://www.qiagen.com/ingenuity.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

