GHRH excess and blockade in X-LAG syndrome
- PMID: 26671997
- PMCID: PMC6300999
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-15-0478
GHRH excess and blockade in X-LAG syndrome
Abstract
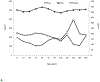
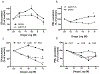
X-linked acrogigantism (X-LAG) syndrome is a newly described form of inheritable pituitary gigantism that begins in early childhood and is usually associated with markedly elevated GH and prolactin secretion by mixed pituitary adenomas/hyperplasia. Microduplications on chromosome Xq26.3 including the GPR101 gene cause X-LAG syndrome. In individual cases random GHRH levels have been elevated. We performed a series of hormonal profiles in a young female sporadic X-LAG syndrome patient and subsequently undertook in vitro studies of primary pituitary tumor culture following neurosurgical resection. The patient demonstrated consistently elevated circulating GHRH levels throughout preoperative testing, which was accompanied by marked GH and prolactin hypersecretion; GH demonstrated a paradoxical increase following TRH administration. In vitro, the pituitary cells showed baseline GH and prolactin release that was further stimulated by GHRH administration. Co-incubation with GHRH and the GHRH receptor antagonist, acetyl-(d-Arg(2))-GHRH (1-29) amide, blocked the GHRH-induced GH stimulation; the GHRH receptor antagonist alone significantly reduced GH release. Pasireotide, but not octreotide, inhibited GH secretion. A ghrelin receptor agonist and an inverse agonist led to modest, statistically significant increases and decreases in GH secretion, respectively. GHRH hypersecretion can accompany the pituitary abnormalities seen in X-LAG syndrome. These data suggest that the pathology of X-LAG syndrome may include hypothalamic dysregulation of GHRH secretion, which is in keeping with localization of GPR101 in the hypothalamus. Therapeutic blockade of GHRH secretion could represent a way to target the marked hormonal hypersecretion and overgrowth that characterizes X-LAG syndrome.
Keywords: GHRH; GPR101; gigantism; growth hormone; pituitary.
© 2016 Society for Endocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures



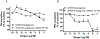
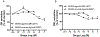
References
-
- Asa SL, Scheithauer BW, Bilbao JM, Horvath E, Ryan N, Kovacs K, Randall RV, Laws ER Jr., Singer W, Linfoot JA, et al. 1984. A case for hypothalamic acromegaly: a clinicopathological study of six patients with hypothalamic gangliocytomas producing growth hormone-releasing factor. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 58 796–803. (doi:10.1210/jcem-58-5-796) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barlier A, Zamora AJ, Grino M, Gunz G, Pellegrini-Bouiller I, Morange-Ramos I, Figarella-Branger D, Dufour H, Jaquet P & Enjalbert A 1999. Expression of functional growth hormone secretagogue receptors in human pituitary adenomas: polymerase chain reaction, triple in-situ hybridization and cell culture studies. Journal of neuroendocrinology 11 491–502 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

