Ultrasound presentation of abdominal non-Hodgkin lymphomas in pediatric patients
- PMID: 26672593
- PMCID: PMC4579673
- DOI: 10.15557/JoU.2013.0040
Ultrasound presentation of abdominal non-Hodgkin lymphomas in pediatric patients
Abstract
Introduction: Burkitt's lymphoma accounts for approximately 25% of lymphomas diagnosed in children of developmental age. The tumor is localized mainly in the intestine (usually in the ileocecal region), mesenteric lymph nodes and extraperitoneal space. The clinical symptoms are non-specific and include: abdominal pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, and acute abdomen suggesting appendicitis or intestinal intussusception. On ultrasound examination, Burkitt's lymphoma may manifest itself in various ways, depending on the origin of the lesion.
Aim: The aim of this paper was to review the ultrasound manifestation of abdominal Burkitt's lymphoma in children.
Material and methods: The analysis included 15 pediatric patients with Burkitt's non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the abdominal cavity. The mean age of the patients was 9.5. Abdominal and gastrointestinal ultrasound examinations were conducted using a Siemens scanner with a convex transducer of 3.5-5 MHz and linear array transducer of L4 - 7.5 MHz.
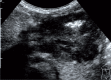
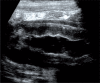
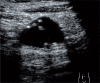
Results: Ultrasound examinations conducted in the group of 15 patients revealed pathological masses localized in the gastric wall in 3 patients (20%), in the ileocecal region in 10 patients (67%) and a disseminated process in 2 patients (13%). In 12 patients with a diagnosed Burkitt's non-Hodgkin lymphoma in an extragastric localization, differences in the morphology of the lesions were observed.
Conclusions: The clinical and ultrasound picture of abdominal Burkitt's lymphoma in children is variable. A careful ultrasound assessment of all abdominal organs conducted with the use of convex and linear probes increases the chances of establishing an adequate diagnosis.
Wprowadzenie: Chłoniak nieziarniczy Burkitta stanowi około 25% chłoniaków wieku rozwojowego. Guz ten lokalizuje się głównie w jelitach (z predyspozycją do okolicy krętniczo-kątniczej), w węzłach chłonnych krezki i przestrzeni pozaotrzewnowej. Objawy kliniczne choroby są niespecyficzne: bóle brzucha, wymioty, krwawienie z przewodu pokarmowego, objawy ostrego brzucha sugerujące zapalenie wyrostka robaczkowego lub wgłobienie jelitowe. W badaniu ultrasonograficznym jamy brzusznej chłoniak Burkitta może mieć różną manifestację, co wiąże się z punktem wyjścia zmiany.
Cel pracy: Celem pracy jest przedstawienie obrazu ultrasonograficznego chłoniaków Burkitta jamy brzusznej u dzieci.
Materiał i metoda: Analizie poddano 15 dzieci z chłoniakiem nieziarniczym Burkitta jamy brzusznej. Średnia wieku pacjentów wynosiła 9,5 roku. Badania ultrasonograficzne jamy brzusznej oraz przewodu pokarmowego wykonano aparatem Siemens, stosując głowicę convex 3,5–5 MHz i liniową L4 – 7,5 MHz.
Wyniki: W badaniu ultrasonograficznym w analizowanej grupie 15 pacjentów u 3 (20%) patologiczna masa zlokalizowana była w ścianie żołądka, u 10 (67%) w okolicy krętniczo-kątniczej, u 2 (13%) proces był rozsiany w jamie brzusznej. U 12 pacjentów z rozpoznanym nieziarniczym chłoniakiem Burkitta w lokalizacji pozażołądkowej stwierdzono różną morfologię zmian w obrazie ultrasonograficznym.
Wnioski: Obraz kliniczny oraz ultrasonograficzny chłoniaka Burkitta jamy brzusznej u dzieci może się różnie manifestować. Dokładna ocena w badaniu ultrasonograficznym wszystkich narządów jamy brzusznej głowicami convex i liniową zwiększa szanse prawidłowego rozpoznania.
Keywords: Burkitt's lymphoma; lymph nodes in children; ultrasound.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Burkitt's lymphoma as a pathological lead point in pediatric intussusception: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025 Jan;126:110710. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110710. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39626432 Free PMC article.
-
Primary intestinal Burkitt's lymphoma in a Syrian child with a challenging initial presentation: A case report and literature review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 3;75:103453. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103453. eCollection 2022 Mar. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35386777 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Acute intussusception in a 2-year-old male patient: a rare case of Burkitt's lymphoma coexisting with Meckel's diverticulum.Front Pediatr. 2024 Dec 5;12:1489118. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1489118. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39703951 Free PMC article.
-
Primary ovarian Burkitt's lymphoma: a rare oncological problem in gynaecology: a review of literature.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017 Oct;296(4):653-660. doi: 10.1007/s00404-017-4478-6. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017. PMID: 28770352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphomas of the gastrointestinal tract: a study of 117 cases presenting with gastrointestinal disease.Cancer. 1978 Aug;42(2):693-707. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197808)42:2<693::aid-cncr2820420241>3.0.co;2-j. Cancer. 1978. PMID: 354774 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary jejunal Burkitt lymphoma in a child: ultrasonic detection.J Surg Case Rep. 2018 May 14;2018(5):rjy090. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjy090. eCollection 2018 May. J Surg Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29770187 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, diagnostic, and prognostic particularities in children - a series of case reports and a review of the literature (CARE compliant).Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Feb;97(8):e9802. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009802. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29465563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burkitt lymphoma as a lead point for jejunojejunal intussusception in a human immunodeficiency virus patient.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug;10(4):342-350. doi: 10.1007/s12328-017-0747-y. Epub 2017 May 18. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28523628 Review.
-
Endosonography and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of high anal fistulae - a comparison.J Ultrason. 2014 Jun;14(57):142-51. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2014.0014. Epub 2014 Jun 30. J Ultrason. 2014. PMID: 26676232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kesik V, Safali M, Citak EC, Kismet E, Koseoglu V. Primary gastric Burkitt lymphoma: a rare cause of intraabdominal mass in childhood. Pediatr Surg Int. 2010;26:927–929. - PubMed
-
- Vural S, Baskin D, Dogan O, Polat N, Caliskan C, Urganci N, et al. Diagnosis in childhood abdominal Burkitt's lymphoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2476–2479. - PubMed
-
- Kamona AA, El-Khatib MA, Swaidan MY, Jarar MS, Suleiman AJ, Ali HM, et al. Pediatric Burkitt's lymphoma: CT findings. Abdom Imaging. 2007;32:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Amodio J, Brodsky JE. Pediatric Burkitt lymphoma presenting as acute pancreatitis: MRI characteristics. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40:770–772. - PubMed
-
- Biko DM, Anupindi SA, Hernandez H, Kersun L, Bellah R. Childhood Burkitt lymphoma: abdominal and pelvic imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192:1304–1315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
