Proximal tubule-targeted heme oxygenase-1 in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 26672618
- PMCID: PMC4868370
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00335.2015
Proximal tubule-targeted heme oxygenase-1 in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
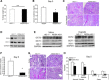
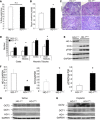
Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is a cytoprotective enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of heme to biliverdin, carbon monoxide, and iron. The beneficial effects of HO-1 expression are not merely due to degradation of the pro-oxidant heme but are also credited to the by-products that have potent, protective effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and prosurvival properties. This is well reflected in the preclinical animal models of injury in both renal and nonrenal settings. However, excessive accumulation of the by-products can be deleterious and lead to mitochondrial toxicity and oxidative stress. Therefore, use of the HO system in alleviating injury merits a targeted approach. Based on the higher susceptibility of the proximal tubule segment of the nephron to injury, we generated transgenic mice using cre-lox technology to enable manipulation of HO-1 (deletion or overexpression) in a cell-specific manner. We demonstrate the validity and feasibility of these mice by breeding them with proximal tubule-specific Cre transgenic mice. Similar to previous reports using chemical modulators and global transgenic mice, we demonstrate that whereas deletion of HO-1, specifically in the proximal tubules, aggravates structural and functional damage during cisplatin nephrotoxicity, selective overexpression of HO-1 in proximal tubules is protective. At the cellular level, cleaved caspase-3 expression, a marker of apoptosis, and p38 signaling were modulated by HO-1. Use of these transgenic mice will aid in the evaluation of the effects of cell-specific HO-1 expression in response to injury and assist in the generation of targeted approaches that will enhance recovery with reduced, unwarranted adverse effects.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; cisplatin; heme oxygenase-1; p38.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelrahman AM, Al Salam S, AlMahruqi AS, Al husseni IS, Mansour MA, Ali BH. N-Acetylcysteine improves renal hemodynamics in rats with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol 30: 15–21, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Balla J, Alam J, Croatt AJ, Nath KA. Induction of heme oxygenase in toxic renal injury: a protective role in cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int 48: 1298–1307, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Nick HS. Renal response to tissue injury: lessons from heme oxygenase-1 GeneAblation and expression. J Am Soc Nephrol 11: 965–973, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

