Errors made in the ultrasound diagnostics of the spleen
- PMID: 26672628
- PMCID: PMC4613572
- DOI: 10.15557/JoU.2013.0005
Errors made in the ultrasound diagnostics of the spleen
Abstract
Ultrasonography, like any imaging method, entails the risk of errors. From among all means of imaging, it is the most subjective and dependent on the examiner's knowledge and experience. This paper presents the causes of examiner-dependent errors as well as those which result from technical settings and preparation of the patient for the examination. Moreover, the authors discuss the most frequent errors in the diagnosis of splenic conditions, which result from insufficient knowledge concerning anatomical variants of this organ, wrong measurements and incorrect examination technique. The mistakes made in the differentiation of focal lesions of the spleen and its hilum are also discussed. Additionally, the differentiation of collateral circulation, lymph nodes and accessory spleens is mentioned. The authors also draw attention to erroneous interpretation of the left liver lobe as a fragment of the spleen as well as the prominent tail of the pancreas filled with gastric contents and intestinal loops as abnormal masses or fluid cisterns in the area of the splenic hilum. Furthermore, the pathologies of the hilum are discussed such as tumors of the splenic flexure of the colon, lesions arising from the left kidney or the left adrenal gland. The authors list characteristic imaging features of the most common focal lesions visualized in a standard ultrasound scan as well as enhancement patterns appearing in contrast-enhanced examinations. The article discusses the features and differentiation of, among others, infarction, splenic cysts including hydatid ones, abscesses and angiomas. The ultrasound appearance of lymphoma and secondary involvement of the spleen by other malignant neoplasms is also mentioned. Moreover, the authors provide useful tips connected with imaging techniques and interpretation of the findings. The ultrasound examination carried out in compliance with current standards allows for an optimal assessment of the organ and reduction of the error-making risk. This article is based on the publication of the experts from the Polish Ultrasound Society of 2005 and updated with the latest findings in pertinent literature. The photographic documentation, which provides images of the discussed lesions, is attached to this article.
Podobnie jak każda metoda obrazowa ultrasonografia niesie ze sobą ryzyko popełniania błędów. Spośród wszystkich badań obrazowych jest ona w największym stopniu subiektywna, zależna od wiedzy i doświadczenia wykonującego badanie. W pracy wskazano przyczyny pomyłek zależne od badającego, ale również od ustawień technicznych i przygotowania pacjenta do badania. Ponadto przedstawiono najczęstsze błędy popełniane w diagnostyce ultrasonograficznej chorób śledziony, wynikające z nieznajomości wariantów anatomicznych jej budowy, nieprawidłowych pomiarów i nieprawidłowej techniki badania. Omówiono pomyłki w różnicowaniu zmian ogniskowych śledziony i jej wnęki. Opisano różnicowanie naczyń krążenia obocznego, węzłów chłonnych oraz śledzion dodatkowych. Zwrócono uwagę na mylną interpretację lewego płata wątroby jako krwiaka śledziony, a także wydatnego ogona trzustki, wypełnionego treścią żołądka lub pętli jelitowych jako nieprawidłowych mas lub zbiorników płynowych w okolicy wnęki śledziony. Ponadto omówiono patologie wnęki, takie jak guz zagięcia śledzionowego jelita grubego, zmiany wychodzące z lewej nerki lub lewego nadnercza. Wymieniono charakterystyczne cechy w obrazowaniu najczęściej spotykanych zmian ogniskowych w standardowym badaniu ultrasonograficznym, jak również wzorce wzmocnienia w badaniach z użyciem środków kontrastowych. Omówiono cechy i różnicowanie m.in. zawału, torbieli śledziony, z uwzględnieniem torbieli bąblowcowych, ropni i naczyniaków. Wspomniano o obrazach ultrasonograficznych w przebiegu chłoniaków oraz wtórnym zajęciu śledziony przez inne nowotwory złośliwe. Artykuł zawiera przydatne wskazówki dotyczące techniki obrazowania oraz interpretacji uzyskanych obrazów. Wykonanie badań zgodnie z obowiązującymi standardami pozwala na optymalną ocenę narządu oraz zminimalizowanie ryzyka popełnienia błędów. Praca została przygotowana na podstawie publikacji ekspertów Polskiego Towarzystwa Ultrasonograficznego z 2005 roku i zaktualizowana o najnowsze doniesienia z piśmiennictwa. Do artykułu dołączono dokumentację zdjęciową obrazującą opisywane zmiany.
Keywords: diagnostic errors; diseases of the spleen; neoplasm of the spleen; splenomegaly; ultrasound diagnostics.
Figures
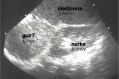




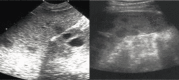
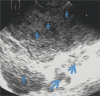


References
-
- Jakubowski W, editor. Praktyczna Ultrasonografia. Warszawa – Zamość: Roztoczańska Szkoła Ultrasonografii; 2005. Błędy i pomyłki w diagnostyce ultrasonograficznej; pp. 124–137.
-
- Jakubowski W, editor. Praktyczna Ultrasonografia. Warszawa – Zamość: Roztoczańska Szkoła Ultrasonografii; 2003. Diagnostyka ultrasonograficzna w gabinecie lekarza rodzinnego; pp. 134–143.
-
- Piscaglia F, Nolsøe C, Dietrich CF, Cosgrove DO, Gilja OH, Bachmann Nielsen M, et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Practice of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS): update 2011 on non-hepatic applications. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33:33–59. - PubMed
-
- Popescu A, Sporea I, Şirli R, Dănilă M, Nicoliţă D, Martie A. The role of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with second generation contrast agents in the evaluation of focal splenic lesions. Med Ultrason. 2009;11:61–65.
-
- von Herbay A, Barreiros AP, Ignee A, Westendorff J, Gregor M, Galle PR, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with SonoVue: differentiation between benign and malignant lesions of the spleen. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28:421–434. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
