Fetal and postnatal ovine mesenteric vascular reactivity
- PMID: 26672733
- PMCID: PMC4837013
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2015.260
Fetal and postnatal ovine mesenteric vascular reactivity
Abstract
Background: Intestinal circulation and mesenteric arterial (MA) reactivity may play a role in preparing the fetus for enteral nutrition. We hypothesized that MA vasoreactivity changes with gestation and vasodilator pathways predominate in the postnatal period.
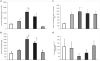
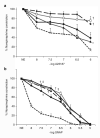
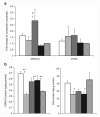
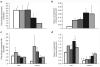
Methods: Small distal MA rings (0.5-mm diameter) were isolated from fetal (116-d, 128-d, 134-d, and 141-d gestation, term ~ 147 d) and postnatal lambs. Vasoreactivity was evaluated using vasoconstrictors (norepinephrine (NE) after pretreatment with propranolol and endothelin-1(ET-1)) and vasodilators (NO donors A23187 and s-nitrosopenicillamine (SNAP)). Protein and mRNA assays for receptors and enzymes (endothelin receptor A, alpha-adrenergic receptor 1A (ADRA1A), endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), and phosphodiesterase5 (PDE5)) were performed in mesenteric arteries.
Results: MA constriction to NE and ET-1 peaked at 134 d. Relaxation to A23187 and SNAP was maximal after birth. Basal eNOS activity was low at 134 d. ADRA1A mRNA and protein increased significantly at 134 d and decreased postnatally. sGC and PDE5 protein increased from 134 to 141 d.
Conclusion: Mesenteric vasoconstriction predominates in late-preterm gestation (134 d; the postconceptional age with the highest incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)) followed by a conversion to vasodilatory influences near the time of full-term birth. Perturbations in this ontogenic mechanism, including preterm birth, may be a risk factor for NEC.
Figures
References
-
- Coombs RC, Morgan ME, Durbin GM, Booth IW, McNeish AS. Doppler assessment of human neonatal gut blood flow velocities: postnatal adaptation and response to feeds. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992;15:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Nankervis CA, Giannone PJ, Reber KM. The neonatal intestinal vasculature: contributing factors to necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Perinatol. 2008;32:83–91. - PubMed
-
- McGrady GA, Rettig PJ, Istre GR, Jason JM, Holman RC, Evatt BL. An outbreak of necrotizing enterocolitis. Association with transfusions of packed red blood cells. Am J Epidemiol. 1987;126:1165–72. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed A, Shah PS. Transfusion associated necrotizing enterocolitis: a meta-analysis of observational data. Pediatrics. 2012;129:529–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

