The Histone Demethylase KDM5 Activates Gene Expression by Recognizing Chromatin Context through Its PHD Reader Motif
- PMID: 26673323
- PMCID: PMC4684901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.007
The Histone Demethylase KDM5 Activates Gene Expression by Recognizing Chromatin Context through Its PHD Reader Motif
Abstract
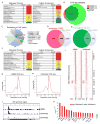
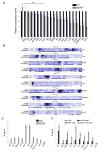
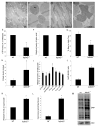
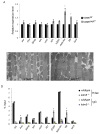
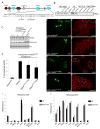
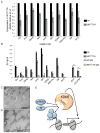
KDM5 family proteins are critically important transcriptional regulators whose physiological functions in the context of a whole animal remain largely unknown. Using genome-wide gene expression and binding analyses in Drosophila adults, we demonstrate that KDM5 (Lid) is a direct regulator of genes required for mitochondrial structure and function. Significantly, this occurs independently of KDM5's well-described JmjC domain-encoded histone demethylase activity. Instead, it requires the PHD motif of KDM5 that binds to histone H3 that is di- or trimethylated on lysine 4 (H3K4me2/3). Genome-wide, KDM5 binding overlaps with the active chromatin mark H3K4me3, and a fly strain specifically lacking H3K4me2/3 binding shows defective KDM5 promoter recruitment and gene activation. KDM5 therefore plays a central role in regulating mitochondrial function by utilizing its ability to recognize specific chromatin contexts. Importantly, KDM5-mediated regulation of mitochondrial activity is likely to be key in human diseases caused by dysfunction of this family of proteins.
Keywords: H3K4me3; KDM5; Lid; PHD motif; histone; mitochondria; transcription.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Histone Demethylase KDM5 Is Essential for Larval Growth in Drosophila.Genetics. 2018 Jul;209(3):773-787. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301004. Epub 2018 May 15. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29764901 Free PMC article.
-
A Drosophila Model of Intellectual Disability Caused by Mutations in the Histone Demethylase KDM5.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 27;22(9):2359-2369. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.018. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29490272 Free PMC article.
-
KDM5-mediated activation of genes required for mitochondrial biology is necessary for viability in Drosophila.Development. 2023 Nov 1;150(21):dev202024. doi: 10.1242/dev.202024. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Development. 2023. PMID: 37800333 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and Interactions of Mammalian KDM5 Demethylases.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 11;13:906662. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.906662. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35899196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Functions of KDM5 in Cancer: Transcriptional Repressor or Activator?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;14(13):3270. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133270. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35805040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H3 binding to the PHD1 domain of histone demethylase KDM5A enables active site remodeling.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 9;10(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07829-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30626866 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila MLR COMPASS complex is essential for programming cis-regulatory information and maintaining epigenetic memory during development.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3476-3495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa082. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32052053 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular events linking variants in the histone demethylase KDM5C to the intellectual disability disorder Claes-Jensen syndrome.FEBS J. 2022 Dec;289(24):7776-7787. doi: 10.1111/febs.16204. Epub 2021 Sep 29. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34536985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of Drosophila Oocyte Determination.J Dev Biol. 2023 May 24;11(2):21. doi: 10.3390/jdb11020021. J Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37367475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutually suppressive roles of KMT2A and KDM5C in behaviour, neuronal structure, and histone H3K4 methylation.Commun Biol. 2020 Jun 1;3(1):278. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-1001-6. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32483278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett A, Santangelo S, Tan K, Catchpole S, Roberts K, Spencer-Dene B, Hall D, Scibetta A, Burchell J, Verdin E, et al. Breast cancer associated transcriptional repressor PLU-1/JARID1B interacts directly with histone deacetylases. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Benevolenskaya EV. Histone H3K4 demethylases are essential in development and differentiation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology-Biochimie Et Biologie Cellulaire. 2007a;85:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Benevolenskaya EV. Retinoblastoma binding protein 2 (RBP2) and differentiation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology-Biochimie Et Biologie Cellulaire. 2007b;85:523–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

