Isotonic Regression Based-Method in Quantitative High-Throughput Screenings for Genotoxicity
- PMID: 26673567
- PMCID: PMC4674159
- DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.13-045.Fujii
Isotonic Regression Based-Method in Quantitative High-Throughput Screenings for Genotoxicity
Abstract
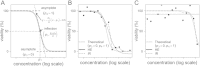
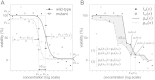
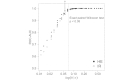
Quantitative high-throughput screenings (qHTSs) for genotoxicity are conducted as part of comprehensive toxicology screening projects. The most widely used method is to compare the dose-response data of a wild-type and DNA repair gene knockout mutants, using model-fitting to the Hill equation (HE). However, this method performs poorly when the observed viability does not fit the equation well, as frequently happens in qHTS. More capable methods must be developed for qHTS where large data variations are unavoidable. In this study, we applied an isotonic regression (IR) method and compared its performance with HE under multiple data conditions. When dose-response data were suitable to draw HE curves with upper and lower asymptotes and experimental random errors were small, HE was better than IR, but when random errors were big, there was no difference between HE and IR. However, when the drawn curves did not have two asymptotes, IR showed better performance (p < 0.05, exact paired Wilcoxon test) with higher specificity (65% in HE vs. 96% in IR). In summary, IR performed similarly to HE when dose-response data were optimal, whereas IR clearly performed better in suboptimal conditions. These findings indicate that IR would be useful in qHTS for comparing dose-response data.
Keywords: Hill equation; Isotonic regression; genotoxicity; quantitative high-throughput screening.
Figures





Similar articles
-
qHTSWaterfall: 3-dimensional visualization software for quantitative high-throughput screening (qHTS) data.J Cheminform. 2023 Mar 31;15(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13321-023-00717-9. J Cheminform. 2023. PMID: 37004072 Free PMC article.
-
Computational tools for fitting the Hill equation to dose-response curves.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2015 Jan-Feb;71:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2015. PMID: 25157754
-
Robust Analysis of High Throughput Screening (HTS) Assay Data.Technometrics. 2013 May 1;55(2):150-160. doi: 10.1080/00401706.2012.749166. Technometrics. 2013. PMID: 23908557 Free PMC article.
-
The comet assay with multiple mouse organs: comparison of comet assay results and carcinogenicity with 208 chemicals selected from the IARC monographs and U.S. NTP Carcinogenicity Database.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000 Nov;30(6):629-799. doi: 10.1080/10408440008951123. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 11145306 Review.
-
Benchmark Dose Modeling of In Vitro Genotoxicity Data: a Reanalysis.Toxicol Res. 2018 Oct;34(4):303-310. doi: 10.5487/TR.2018.34.4.303. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Toxicol Res. 2018. PMID: 30370005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estimating Potency in High-Throughput Screening Experiments by Maximizing the Rate of Change in Weighted Shannon Entropy.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 15;6:27897. doi: 10.1038/srep27897. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27302286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Best MJ, Chakravarti N. 1990. Active set algorithms for isotonic regression; a unifying framework. Mathematical Programming 47:425–39.
-
- Byrd RH, Byrd RH, Lu P, Lu P, Nocedal J, Nocedal J, Zhu C. 1994. A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 16:1190–208.
-
- DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. 1988. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics Sep(44(3)):837–45. - PubMed
-
- Evans TJ, Yamamoto KN, Hirota K, Takeda S. 2010. Mutant cells defective in DNA repair pathways provide a sensitive high-throughput assay for genotoxicity. DNA Repair (12):1292–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

