Readers of poly(ADP-ribose): designed to be fit for purpose
- PMID: 26673700
- PMCID: PMC4756826
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1383
Readers of poly(ADP-ribose): designed to be fit for purpose
Abstract
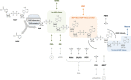
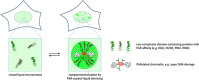
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) regulate many aspects of protein function and are indispensable for the spatio-temporal regulation of cellular processes. The proteome-wide identification of PTM targets has made significant progress in recent years, as has the characterization of their writers, readers, modifiers and erasers. One of the most elusive PTMs is poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation), a nucleic acid-like PTM involved in chromatin dynamics, genome stability maintenance, transcription, cell metabolism and development. In this article, we provide an overview on our current understanding of the writers of this modification and their targets, as well as the enzymes that degrade and thereby modify and erase poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR). Since many cellular functions of PARylation are exerted through dynamic interactions of PAR-binding proteins with PAR, we discuss the readers of this modification and provide a synthesis of recent findings, which suggest that multiple structurally highly diverse reader modules, ranging from completely folded PAR-binding domains to intrinsically disordered sequence stretches, evolved as PAR effectors to carry out specific cellular functions.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Schreiber V., Dantzer F., Ame J.C., de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:517–528. - PubMed
-
- Burkle A. Poly(ADP-ribose). The most elaborate metabolite of NAD+ FEBS J. 2005;272:4576–4589. - PubMed
-
- Hassa P.O., Hottiger M.O. The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:3046–3082. - PubMed
-
- Barkauskaite E., Jankevicius G., Ladurner A.G., Ahel I., Timinszky G. The recognition and removal of cellular poly(ADP-ribose) signals. FEBS J. 2013;280:3491–3507. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P., Weill J.D., Mandel P. Nicotinamide mononucleotide activation of new DNA-dependent polyadenylic acid synthesizing nuclear enzyme. Bioch. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1963;11:39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

