Different duplex/quadruplex junctions determine the properties of anti-thrombin aptamers with mixed folding
- PMID: 26673709
- PMCID: PMC4737158
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1384
Different duplex/quadruplex junctions determine the properties of anti-thrombin aptamers with mixed folding
Erratum in
-
Different duplex/quadruplex junctions determine the properties of anti-thrombin aptamers with mixed folding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 May 5;44(8):3969. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw078. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 31095328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
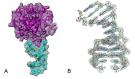
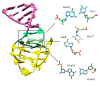
Mixed duplex/quadruplex oligonucleotides have attracted great interest as therapeutic targets as well as effective biomedical aptamers. In the case of thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA), the addition of a duplex motif to the G-quadruplex module improves the aptamer resistance to biodegradation and the affinity for thrombin. In particular, the mixed oligonucleotide RE31 is significantly more effective than TBA in anticoagulation experiments and shows a slower disappearance rate in human plasma and blood. In the crystal structure of the complex with thrombin, RE31 adopts an elongated structure in which the duplex and quadruplex regions are perfectly stacked on top of each other, firmly connected by a well-structured junction. The lock-and-key shape complementarity between the TT loops of the G-quadruplex and the protein exosite I gives rise to the basic interaction that stabilizes the complex. However, our data suggest that the duplex motif may have an active role in determining the greater anti-thrombin activity in biological fluids with respect to TBA. This work gives new information on mixed oligonucleotides and highlights the importance of structural data on duplex/quadruplex junctions, which appear to be varied, unpredictable, and fundamental in determining the aptamer functional properties.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
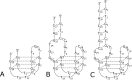
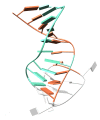
Similar articles
-
Duplex-quadruplex motifs in a peculiar structural organization cooperatively contribute to thrombin binding of a DNA aptamer.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Dec;69(Pt 12):2403-11. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913022269. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 24311581
-
Duplex/quadruplex oligonucleotides: Role of the duplex domain in the stabilization of a new generation of highly effective anti-thrombin aptamers.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):1697-1705. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.033. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29024684
-
Cation Coordination Alters the Conformation of a Thrombin-Binding G-Quadruplex DNA Aptamer That Affects Inhibition of Thrombin.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016 Oct;26(5):299-308. doi: 10.1089/nat.2016.0606. Epub 2016 May 9. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016. PMID: 27159247
-
G-quadruplex-based aptamers targeting human thrombin: Discovery, chemical modifications and antithrombotic effects.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;217:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107649. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32777331 Review.
-
Thrombin binding aptamer, more than a simple aptamer: chemically modified derivatives and biomedical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(14):2036-47. doi: 10.2174/138161212799958387. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22376107 Review.
Cited by
-
Putative Mechanisms Underlying High Inhibitory Activities of Bimodular DNA Aptamers to Thrombin.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 24;9(2):41. doi: 10.3390/biom9020041. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30682825 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Biology for the Molecular Insight between Aptamers and Target Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4093. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084093. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steric hindrance and structural flexibility shape the functional properties of a guanine-rich oligonucleotide.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Sep 8;51(16):8880-8890. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad634. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37503836 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of thrombin in complex with chemically modified thrombin DNA aptamers reveal the origins of enhanced affinity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 May 18;46(9):4819-4830. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky268. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29684204 Free PMC article.
-
High-affinity binding at quadruplex-duplex junctions: rather the rule than the exception.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 11;50(20):11948-11964. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1088. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36416262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh A., Bansal M. A glossary of DNA structures from A to Z. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003;59:620–626. - PubMed
-
- Leslie A.G., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R.L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J. Mol. Biol. 1980;143:49–72. - PubMed
-
- Lilley D.M., Clegg R.M. The structure of the four-way junction in DNA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1993;22:299–328. - PubMed
-
- Gueron M., Leroy J.L. The i-motif in nucleic acids. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000;10:326–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

