Roquin--a multifunctional regulator of immune homeostasis
- PMID: 26673963
- PMCID: PMC4777649
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2015.58
Roquin--a multifunctional regulator of immune homeostasis
Abstract
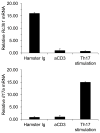
Roquin-1 (Rc3h1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase originally discovered in a mutational screen for genetic factors contributory to systemic lupus erythematosus-like symptoms in mice. A single base-pair mutation in the Rc3h1 gene resulted in the manifestation of autoantibody production and sustained immunological inflammation characterized by excessive T follicular helper cell activation and formation of germinal centers. Subsequent studies have uncovered a multifactorial process by which Roquin-1 contributes to the maintenance of immune homeostasis. Through its interactions with partner proteins, Roquin-1 targets mRNAs for decay with inducible costimulator being a primary target. In this review, we discuss newly discovered functions of Roquin-1 in the immune system and inflammation, and in disease manifestation, and discuss avenues of further research. A model is presented for the role of Roquin in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
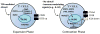
References
-
- Yu D, Tan AH, Hu X, Athanasopoulos V, Simpson N, Silva DG, et al. Roquin represses autoimmunity by limiting inducible T-cell co-stimulator messenger RNA. Nature. 2007;450(7167):299–303. - PubMed
-
- Vinuesa CG, Cook MC, Angelucci C, Athanasopoulos V, Rui L, Hill KM, et al. A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature. 2005;435(7041):452–8. - PubMed
-
- Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A, Melino G. The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: multiple players in cancer development. Cancer cell. 2008;14(1):10–21. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Gao B, Lee SM, Bennett K, Fang D. RLE-1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, regulates C. elegans aging by catalyzing DAF-16 polyubiquitination. Developmental cell. 2007;12(2):235–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

