Cdk1 orders mitotic events through coordination of a chromosome-associated phosphatase switch
- PMID: 26674376
- PMCID: PMC4703885
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10215
Cdk1 orders mitotic events through coordination of a chromosome-associated phosphatase switch
Abstract
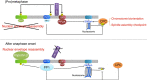
RepoMan is a scaffold for signalling by mitotic phosphatases at the chromosomes. During (pro)metaphase, RepoMan-associated protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A-B56 regulate the chromosome targeting of Aurora-B kinase and RepoMan, respectively. Here we show that this task division is critically dependent on the phosphorylation of RepoMan by protein kinase Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1), which reduces the binding of PP1 but facilitates the recruitment of PP2A-B56. The inactivation of Cdk1 in early anaphase reverses this phosphatase switch, resulting in the accumulation of PP1-RepoMan to a level that is sufficient to catalyse its own chromosome targeting in a PP2A-independent and irreversible manner. Bulk-targeted PP1-RepoMan also inactivates Aurora B and initiates nuclear-envelope reassembly through dephosphorylation-mediated recruitment of Importin β. Bypassing the Cdk1 regulation of PP1-RepoMan causes the premature dephosphorylation of its mitotic-exit substrates in prometaphase. Hence, the regulation of RepoMan-associated phosphatases by Cdk1 is essential for the timely dephosphorylation of their mitotic substrates.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

