High density lipoproteins: Measurement techniques and potential biomarkers of cardiovascular risk
- PMID: 26674734
- PMCID: PMC4661556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2015.01.005
High density lipoproteins: Measurement techniques and potential biomarkers of cardiovascular risk
Abstract
Plasma high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) comprises a heterogeneous family of lipoprotein species, differing in surface charge, size and lipid and protein compositions. While HDL cholesterol (C) mass is a strong, graded and coherent biomarker of cardiovascular risk, genetic and clinical trial data suggest that the simple measurement of HDL-C may not be causal in preventing atherosclerosis nor reflect HDL functionality. Indeed, the measurement of HDL-C may be a biomarker of cardiovascular health. To assess the issue of HDL function as a potential therapeutic target, robust and simple analytical methods are required. The complex pleiotropic effects of HDL make the development of a single measurement challenging. Development of laboratory assays that accurately HDL function must be developed validated and brought to high-throughput for clinical purposes. This review discusses the limitations of current laboratory technologies for methods that separate and quantify HDL and potential application to predict CVD, with an emphasis on emergent approaches as potential biomarkers in clinical practice.
Keywords: 2D-PAGGE, two dimensional polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis; ApoA-I, apolipoprotein A-I; Apolipoprotein A-I; Atherosclerosis; Biomarkers of cardiovascular risk; CHD, coronary heart disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; Cellular cholesterol efflux; Coronary artery disease; HDL, high density lipoprotein; HPLC, High Performance Liquid Chromatography; High density lipoproteins; LCAT, lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase; LDL, low density lipoprotein; MALDI, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization; MOP, myeloperoxidase; MS/MS, tandem-mass spectrometry; ND-PAGGE, non-denaturant polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PON1, paraoxonase 1; SELDI, surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization; TOF, time-of-flight; UTC, ultracentrifugation; Vascular endothelial function.
Figures

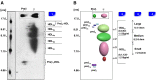

Similar articles
-
Update on the laboratory investigation of dyslipidemias.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Apr;479:103-125. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29336935 Review.
-
Activation of paraoxonase 1 is associated with HDL remodeling ex vivo.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Feb 15;429:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.021. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24280342
-
Mass spectrometry-based analytical tools for the molecular protein characterization of human plasma lipoproteins.Proteomics. 2005 Jul;5(10):2619-30. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200401233. Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 15892164
-
Apolipoprotein A-I configuration and cell cholesterol efflux activity of discoidal lipoproteins depend on the reconstitution process.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1841(1):180-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.017. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24201377
-
Non-HDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B compared with LDL-cholesterol in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment.Pathology. 2019 Feb;51(2):148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Pathology. 2019. PMID: 30595507 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of improved fat meat products consumption on emergent cardiovascular disease markers of male volunteers at cardiovascular risk.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Dec;72(4):669-678. doi: 10.1007/s13105-016-0505-5. Epub 2016 Jul 4. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27376533
-
Cholesterol Transport Dysfunction and Its Involvement in Atherogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1332. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031332. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDL in Endocrine Carcinomas: Biomarker, Drug Carrier, and Potential Therapeutic.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Nov 30;9:715. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00715. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30555417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative evaluation of cardiac and neurological safety status of two commonly used oral hypoglycaemic agents in T2-DM Swiss albino mice model.Metabol Open. 2022 May 23;14:100191. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100191. eCollection 2022 Jun. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 35651883 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the size and electrophoretic mobility of HDL subpopulation particles in chronic kidney disease.J Nephrol. 2023 Jan;36(1):115-124. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01412-y. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 35943666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boekholdt S.M., Arsenault B.J., Hovingh G.K., Mora S., Pedersen T.R., Larosa J.C., Welch K.M., Amarenco P., Demicco D.A., Tonkin A.M. Levels and changes of HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein A-I in relation to risk of cardiovascular events among statin-treated patients: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2013;128:1504–1512. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toth P.P., Barter P.J., Rosenson R.S., Boden W.E., Chapman M.J., Cuchel M., D'Agostino R.B., Sr., Davidson M.H., Davidson W.S., Heinecke J.W. High-density lipoproteins: a consensus statement from the National Lipid Association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013;7:484–525. - PubMed
-
- Rader D.J. Spotlight on HDL biology: new insights in metabolism, function, and translation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014;103:337–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

