Skeletal muscle as a therapeutic target for delaying type 1 diabetic complications
- PMID: 26674848
- PMCID: PMC4673386
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i17.1323
Skeletal muscle as a therapeutic target for delaying type 1 diabetic complications
Abstract
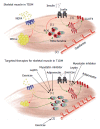
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic autoimmune disease targeting the pancreatic beta-cells and rendering the person hypoinsulinemic and hyperglycemic. Despite exogenous insulin therapy, individuals with T1DM will invariably develop long-term complications such as blindness, kidney failure and cardiovascular disease. Though often overlooked, skeletal muscle is also adversely affected in T1DM, with both physical and metabolic derangements reported. As the largest metabolic organ in the body, impairments to skeletal muscle health in T1DM would impact insulin sensitivity, glucose/lipid disposal and basal metabolic rate and thus affect the ability of persons with T1DM to manage their disease. In this review, we discuss the impact of T1DM on skeletal muscle health with a particular focus on the proposed mechanisms involved. We then identify and discuss established and potential adjuvant therapies which, in association with insulin therapy, would improve the health of skeletal muscle in those with T1DM and thereby improve disease management- ultimately delaying the onset and severity of other long-term diabetic complications.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Exercise; Leptin; Metabolism; Myostatin; Skeletal muscle; Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Iscoe KE, Campbell JE, Jamnik V, Perkins BA, Riddell MC. Efficacy of continuous real-time blood glucose monitoring during and after prolonged high-intensity cycling exercise: spinning with a continuous glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2006;8:627–635. - PubMed
-
- Katz LD, Glickman MG, Rapoport S, Ferrannini E, DeFronzo RA. Splanchnic and peripheral disposal of oral glucose in man. Diabetes. 1983;32:675–679. - PubMed
-
- Kraegen EW, James DE, Jenkins AB, Chisholm DJ. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985;248:E353–E362. - PubMed
-
- Baron AD, Brechtel G, Wallace P, Edelman SV. Rates and tissue sites of non-insulin- and insulin-mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988;255:E769–E774. - PubMed
-
- Krause MP, Riddell MC, Gordon CS, Imam SA, Cafarelli E, Hawke TJ. Diabetic myopathy differs between Ins2Akita+/- and streptozotocin-induced Type 1 diabetic models. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2009;106:1650–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

