Evaluation of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Colombian population: A longitudinal observational study
- PMID: 26675051
- PMCID: PMC4673387
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i17.1337
Evaluation of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Colombian population: A longitudinal observational study
Abstract
Aim: To assess the performance of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC) questionnaire for detecting and predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) in a Colombian population.
Methods: This is a longitudinal observational study conducted in Floridablanca, Colombia. Adult subjects (age ≥ 35 years) without known diabetes, were included. A modified version of FINDRISC was completed, and the glycemia values from all the subjects were collected from the hospital's database. Firstly, a cross-sectional analysis was performed and then, the subsample of prediabetic participants was followed for diabetes incidence.
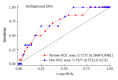
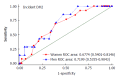
Results: A total of 772 subjects were suitable for the study. The overall prevalence of undiagnosed DM2 was 2.59%, and the incidence of DM2 among the prediabetic participants was 7.5 per 100 person-years after a total of 265257 person-years follow-up. The FINDRISC at baseline was significantly associated with undiagnosed and incident DM2. The area under receiver operating characteristics curve of the FINDRISC score for detecting undiagnosed DM2 in both men and women was 0.7477 and 0.7175, respectively; and for predicting the incidence of DM2 among prediabetics was 71.99% in men and 67.74% in women.
Conclusion: The FINDRISC questionnaire is a useful screening tool to identify cross-sectionally unknown DM2 and to predict the incidence of DM2 among prediabetics in the Colombian population.
Keywords: Colombia; Finnish diabetes risk score; Prediabetes; Screening; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- López-Jaramillo P, Gómez-Arbeláez D, Camacho PA, Álvarez J, Molina DI, Sánchez G, Arcos E, Narváez C, García H, Pérez M, et al. Prevalencia, conocimiento, tratamiento y control de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en Colombia. Resultados del estudio PURE-Colombia. Rev Colomb Cardiol. 2013;20:16.
-
- Narayan KM, Gregg EW, Fagot-Campagna A, Engelgau MM, Vinicor F. Diabetes--a common, growing, serious, costly, and potentially preventable public health problem. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000;50 Suppl 2:S77–S84. - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1343–1350. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

