Tuft-cell-derived IL-25 regulates an intestinal ILC2-epithelial response circuit
- PMID: 26675736
- PMCID: PMC4830391
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16161
Tuft-cell-derived IL-25 regulates an intestinal ILC2-epithelial response circuit
Abstract
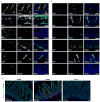
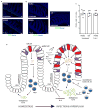
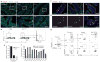
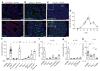
Parasitic helminths and allergens induce a type 2 immune response leading to profound changes in tissue physiology, including hyperplasia of mucus-secreting goblet cells and smooth muscle hypercontractility. This response, known as 'weep and sweep', requires interleukin (IL)-13 production by tissue-resident group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and recruited type 2 helper T cells (TH2 cells). Experiments in mice and humans have demonstrated requirements for the epithelial cytokines IL-33, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and IL-25 in the activation of ILC2s, but the sources and regulation of these signals remain poorly defined. In the small intestine, the epithelium consists of at least five distinct cellular lineages, including the tuft cell, whose function is unclear. Here we show that tuft cells constitutively express IL-25 to sustain ILC2 homeostasis in the resting lamina propria in mice. After helminth infection, tuft-cell-derived IL-25 further activates ILC2s to secrete IL-13, which acts on epithelial crypt progenitors to promote differentiation of tuft and goblet cells, leading to increased frequencies of both. Tuft cells, ILC2s and epithelial progenitors therefore comprise a response circuit that mediates epithelial remodelling associated with type 2 immunity in the small intestine, and perhaps at other mucosal barriers populated by these cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
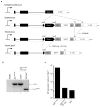
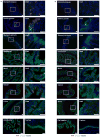

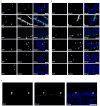

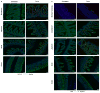


Comment in
-
Tuft cell-derived IL-25 activates and maintains ILC2.Immunol Cell Biol. 2016 Mar;94(3):221-3. doi: 10.1038/icb.2016.10. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26975341 No abstract available.
-
Tuft Cells: A New Flavor in Innate Epithelial Immunity.Trends Parasitol. 2016 Aug;32(8):583-585. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 5. Trends Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27161767
References
-
- Miller HR, Nawa Y. Immune regulation of intestinal goblet cell differentiation. Specific induction of nonspecific protection against helminths? Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1979;21:31–45. - PubMed
-
- Castro GA, Badial-Aceves F, Smith JW, Dudrick SJ, Weisbrodt NW. Altered small bowel propulsion associated with parasitism. Gastroenterology. 1976;71:620–625. - PubMed
-
- Grencis RK. Immunity to helminths: resistance, regulation, and susceptibility to gastrointestinal nematodes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:201–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

