Myc Induces miRNA-Mediated Apoptosis in Response to HDAC Inhibition in Hematologic Malignancies
- PMID: 26676759
- PMCID: PMC4738141
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1751
Myc Induces miRNA-Mediated Apoptosis in Response to HDAC Inhibition in Hematologic Malignancies
Erratum in
-
Correction: Myc Induces miRNA-Mediated Apoptosis in Response to HDAC Inhibition in Hematologic Malignancies.Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 1;77(23):6789. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3215. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29196417 No abstract available.
Abstract
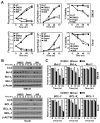
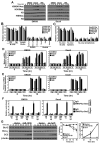
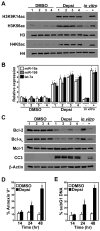
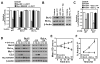
Alterations in the expression or function of histone deacetylases (HDAC) contribute to the development and progression of hematologic malignancies. Consequently, the development and implementation of HDAC inhibitors has proven to be therapeutically beneficial, particularly for hematologic malignancies. However, the molecular mechanisms by which HDAC inhibition (HDACi) induces tumor cell death remain unresolved. Here, we investigated the effects of HDACi in Myc-driven B-cell lymphoma and five other hematopoietic malignancies. We determined that Myc-mediated transcriptional repression of the miR-15 and let-7 families in malignant cells was relieved upon HDACi, and Myc was required for their upregulation. The miR-15 and let-7 families then targeted and downregulated the antiapoptotic genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, respectively, to induce HDACi-mediated apoptosis. Notably, Myc also transcriptionally upregulated these miRNA in untransformed cells, indicating that this Myc-induced miRNA-mediated apoptotic pathway is suppressed in malignant cells, but becomes reactivated upon HDACi. Taken together, our results reveal a previously unknown mechanism by which Myc induces apoptosis independent of the p53 pathway and as a response to HDACi in malignant hematopoietic cells.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

