The implications of autoantibodies to a single islet antigen in relatives with normal glucose tolerance: development of other autoantibodies and progression to type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 26676824
- PMCID: PMC4742489
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-015-3830-2
The implications of autoantibodies to a single islet antigen in relatives with normal glucose tolerance: development of other autoantibodies and progression to type 1 diabetes
Abstract
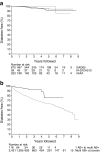
Aims/hypothesis: Autoantibodies directed at single islet autoantigens are associated with lower overall risk of type 1 diabetes than multiple autoantibodies, but individuals with one autoantibody may progress to higher risk categories. We examined the characteristics of this progression in relatives followed prospectively in the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention.
Methods: The study population comprised 983 relatives who were single autoantibody positive with normal baseline glucose tolerance (median age 16.2 years). Samples were screened for antibodies to GAD, insulinoma-associated antigen 2 (IA-2) and insulin, and all positive samples tested for antibodies to zinc transporter 8 and islet cell antibodies.
Results: Antibodies to at least one additional islet autoantigen appeared in 118 of 983 relatives (overall 5 year risk 22%, 95% CI [17.9, 26.1]). At baseline, antibodies to GAD alone (68%) were more frequent than antibodies to insulin (26%) or IA-2 (6%), but all were associated with a similar risk of developing additional autoantibodies. Risk was associated with younger age (p = 0.002) and HLA class II genotype, but was similar in high and intermediate genetic risk groups (p = 0.65). Relatives who became multiple autoantibody positive during the follow-up had increased risk of developing diabetes comparable with the risk in relatives with multiple autoantibodies at study entry.
Conclusions/interpretation: Progression of islet autoimmunity in single autoantibody positive relatives in late childhood/adult life is associated with a predominance of autoantibodies to GAD and a distinct HLA risk profile. This heterogeneity in type 1 diabetes autoimmunity has potentially important implications for disease prevention.
Keywords: Autoantigens; Diabetes antibodies; GAD; HLA; IA-2; Insulin autoantibodies; Islet autoantibodies; Prediction; Prevention; Zinc transporter 8.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001085/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK084565/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001105/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

