PAL SPME Arrow--evaluation of a novel solid-phase microextraction device for freely dissolved PAHs in water
- PMID: 26677018
- PMCID: PMC4709367
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-015-9187-z
PAL SPME Arrow--evaluation of a novel solid-phase microextraction device for freely dissolved PAHs in water
Abstract
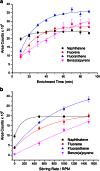
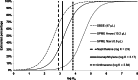
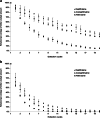
After more than 25 years, solid-phase microextraction (SPME) has gained widespread acceptance as a well-automatable and flexible microextraction technique, while its instrumental basis remained mostly unchanged. The novel PAL (Prep And Load solution) SPME Arrow combines the advantages of SPME with the benefits of extraction techniques providing larger sorption phase volumes such as stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE). It thereby avoids the inherent drawbacks of both techniques such as limitations in method automation in the case of SBSE, as well as the small sorption phase volumes and the lacking fiber robustness of classical SPME fibers. This new design is based on a robust stainless steel backbone, carrying, the screw connection to the PAL sampler, the enlarged sorption phase, and an arrow-shaped tip for conservative penetration of septa (hence the name). An outer capillary encloses this phase apart from enrichment and desorption processes and rests against the tip during transfer and penetrations, resulting in a homogeneously closed device. Here, we present an evaluation and a comparison of the novel PAL SPME Arrow with classical SPME fibers, extracting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) as model analytes, from the freely dissolved fraction in lab water and groundwater via direct immersion using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) as common sorption phase material. Limits of detection, repeatabilities, and extraction yields were determined for the PAL SPME Arrow and compared to data of classical SPME fibers and SBSE bars. Results indicate a significant benefit in extraction efficiency due to the larger sorption phase volume. It is accompanied by faultless mechanical robustness and thus better reliability, especially in case of prolonged, unattended, and automated operation. As an exemplary application, the water-soluble fraction of PAHs and derivatives in a roofing felt sample was quantified.
Keywords: Microextraction; PAH; PAL SPME Arrow; PDMS; SPME.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potentialities of two solventless extraction approaches--stir bar sorptive extraction and headspace solid-phase microextraction for determination of higher alcohol acetates, isoamyl esters and ethyl esters in wines.Talanta. 2009 Dec 15;80(2):622-30. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2009.07.038. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Talanta. 2009. PMID: 19836529
-
Solid-phase microextraction and headspace solid-phase microextraction for the determination of high molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and soil samples.J Chromatogr Sci. 2000 Dec;38(12):528-34. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/38.12.528. J Chromatogr Sci. 2000. PMID: 11144512
-
Systematic comparison of static and dynamic headspace sampling techniques for gas chromatography.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016 Sep;408(24):6567-79. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9843-y. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016. PMID: 27526093
-
Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phase microextraction techniques.Talanta. 2014 Feb;119:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.050. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24401382 Review.
-
Solventless Microextration Techniques for Pharmaceutical Analysis: The Greener Solution.Front Chem. 2022 Jan 13;9:785830. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.785830. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35096766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in solid phase microextraction with various geometries in environmental analysis.RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 30;14(38):27608-27621. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03251a. eCollection 2024 Aug 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39221126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of a new coating of graphene oxide/nickel complex on a nickelized metal surface for direct immersion solid phase microextraction of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.BMC Chem. 2021 Oct 16;15(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13065-021-00783-w. BMC Chem. 2021. PMID: 34656161 Free PMC article.
-
Isotope-labeling in situ derivatization and HS-SPME arrow GC-MS/MS for simultaneous determination of fatty acids and fatty acid methyl esters in aqueous matrices.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Nov;415(26):6525-6536. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04930-1. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37740751 Free PMC article.
-
Review of recent developments in GC-MS approaches to metabolomics-based research.Metabolomics. 2018 Nov 17;14(11):152. doi: 10.1007/s11306-018-1449-2. Metabolomics. 2018. PMID: 30830421 Review.
-
Exploring different high-capacity tools and extraction modes to characterize the aroma of brewed coffee.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Jul;415(18):4501-4510. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04654-2. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37041278
References
-
- Belardi RP, Pawliszyn JB. The application of chemically modified fused silica fibers in the extraction of organics from water matrix samples and their rapid transfer to capillary columns. Water Pollut Res J Can. 1989;24:179–191.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

