Docetaxel-related interstitial pneumonitis
- PMID: 26677333
- PMCID: PMC4677769
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S90488
Docetaxel-related interstitial pneumonitis
Abstract
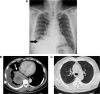
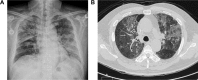
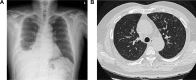
Docetaxel (Taxotere(®)) is an agent that is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. In recent years, docetaxel-related interstitial lung disease (ILD) has been reported in several case series studies. The onset of ILD occurred ~10-20 days (median time: 18 days) after docetaxel administration. Here, we reported the case of a patient who had pulmonary toxicity of ILD within 3 days after using a relatively low-dose docetaxel administration. Although some articles have described patients who progressed to respiratory failure and needed intubation, this patient responded well to steroid treatment and discontinued docetaxel administration.
Keywords: docetaxel; interstitial lung disease.
Figures
References
-
- Eivind S, Gunhild H, Karsten G, et al. Lethal pneumonitis after docetaxel chemotherapy: case report and review of the literature. Acta Oncol. 2013;52:1034–1038. - PubMed
-
- Read WL, Mortimer JE, Picus J. Severe interstitial pneumonitis associated with docetaxel administration. Cancer. 2002;94:847–853. - PubMed
-
- Chen YM, Shih JF, Perng RP, Tsai CM, Whang-Peng J. A randomized trial of different docetaxel schedules in non-small cell lung cancer patients who failed previous platinum-based chemotherapy. Chest. 2006;129:1031–1038. - PubMed
-
- Tamiya A, Naito T, Miura S, et al. Interstitial lung disease associated with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:1103–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

