Minireview: Mouse Models of Rho GTPase Function in Mammary Gland Development, Tumorigenesis, and Metastasis
- PMID: 26677753
- PMCID: PMC4771699
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2015-1294
Minireview: Mouse Models of Rho GTPase Function in Mammary Gland Development, Tumorigenesis, and Metastasis
Abstract
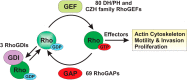
Ras homolog (Rho) family small GTPases are critical regulators of actin cytoskeletal organization, cell motility, proliferation, and survival. Surprisingly, the large majority of the studies underlying our knowledge of Rho protein function have been carried out in cultured cells, and it is only recently that researchers have begun to assess Rho GTPase regulation and function in vivo. The purpose of this review is to evaluate our current knowledge of Rho GTPase function in mouse mammary gland development, tumorigenesis and metastasis. Although our knowledge is still incomplete, these studies are already uncovering important themes as to the physiological roles of Rho GTPase signaling in normal mammary gland development and function. Essential contributions of Rho proteins to breast cancer initiation, tumor progression, and metastatic dissemination have also been identified.
Figures


References
-
- Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:247–269. - PubMed
-
- Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ. Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:690–701. - PubMed
-
- Thumkeo D, Watanabe S, Narumiya S. Physiological roles of Rho and Rho effectors in mammals. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013;92:303–315. - PubMed
-
- Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J. GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:167–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

