The Inflammatory Transcription Factors NFκB, STAT1 and STAT3 Drive Age-Associated Transcriptional Changes in the Human Kidney
- PMID: 26678048
- PMCID: PMC4682820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005734
The Inflammatory Transcription Factors NFκB, STAT1 and STAT3 Drive Age-Associated Transcriptional Changes in the Human Kidney
Abstract
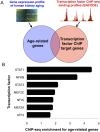
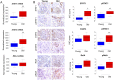
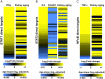
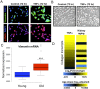
Human kidney function declines with age, accompanied by stereotyped changes in gene expression and histopathology, but the mechanisms underlying these changes are largely unknown. To identify potential regulators of kidney aging, we compared age-associated transcriptional changes in the human kidney with genome-wide maps of transcription factor occupancy from ChIP-seq datasets in human cells. The strongest candidates were the inflammation-associated transcription factors NFκB, STAT1 and STAT3, the activities of which increase with age in epithelial compartments of the renal cortex. Stimulation of renal tubular epithelial cells with the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 (a STAT3 activator), IFNγ (a STAT1 activator), or TNFα (an NFκB activator) recapitulated age-associated gene expression changes. We show that common DNA variants in RELA and NFKB1, the two genes encoding subunits of the NFκB transcription factor, associate with kidney function and chronic kidney disease in gene association studies, providing the first evidence that genetic variation in NFκB contributes to renal aging phenotypes. Our results suggest that NFκB, STAT1 and STAT3 underlie transcriptional changes and chronic inflammation in the aging human kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bolignano D, Mattace-Raso F, Sijbrands EJG, Zoccali C (2014) The aging kidney revisited: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev 14C: 65–80. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS (2003) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 41: 1–12. - PubMed
-
- van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh J, Astor BC, Woodward M, et al. (2011) Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int 79: 1341–1352. 10.1038/ki.2010.536 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

