Febuxostat-induced acute liver injury
- PMID: 26679098
- PMCID: PMC4764455
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.28403
Febuxostat-induced acute liver injury
Figures

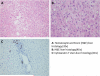
Similar articles
-
Acute hepatitis secondary to febuxostat.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2025 Jul;117(7):414-415. doi: 10.17235/reed.2023.10047/2023. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2025. PMID: 37982551
-
Desensitization to febuxostat: report of two cases.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015 Jul-Aug;3(4):633-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2015.01.022. Epub 2015 Mar 7. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015. PMID: 25758914 No abstract available.
-
Fixed drug eruption-like macules caused by febuxostat.Eur J Dermatol. 2016 Aug 1;26(4):412-3. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2016.2796. Eur J Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27211520 No abstract available.
-
Febuxostat for the chronic management of hyperuricemia in patients with gout.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9(5):665-73. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2016.1162094. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26942273 Review.
-
Hypercalcemia worsened by the use of furosemide in a patient suffering from allopurinol-induced granulomatous hepatitis.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2010 Feb;102(2):147-8. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2010. PMID: 20361854 Review. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hyperuricemia-Related Diseases and Xanthine Oxidoreductase (XOR) Inhibitors: An Overview.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Jul 17;22:2501-12. doi: 10.12659/msm.899852. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27423335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Modified Taxifolin Liposomes Promote Liver Repair by Modulating Autophagy to Inhibit Activation of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 1;10:860515. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.860515. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35721857 Free PMC article.
-
Isoorientin exerts a urate-lowering effect through inhibition of xanthine oxidase and regulation of the TLR4-NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway.J Nat Med. 2021 Jan;75(1):129-141. doi: 10.1007/s11418-020-01464-z. Epub 2020 Nov 13. J Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 33188510
-
From purines to purinergic signalling: molecular functions and human diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Apr 28;6(1):162. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00553-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33907179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of Hepatotoxicity in Patients With Gout Treated With Febuxostat or Benzbromarone: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025 Sep;77(9):1149-1156. doi: 10.1002/acr.25547. Epub 2025 May 8. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40195679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruce SP. Febuxostat: a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40:2187–94. - PubMed
-
- Becker MA, Schumacher HR, MacDonald PA, Lloyd E, Lademacher C. Clinical efficacy and safety of successful longterm urate lowering with febuxostat or allopurinol in patients with gout. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:1273–82. - PubMed
-
- Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Jr., Wortmann RL, MacDonald PA, Palo WA, Eustace D, Vernillet L, Joseph-Ridge N. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2450–61. - PubMed
-
- Febuxostat. http://livertox.nlm.nih.gov [last accessed August 10, 2014]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

