Rabphilin 3A retains NMDA receptors at synaptic sites through interaction with GluN2A/PSD-95 complex
- PMID: 26679993
- PMCID: PMC4703873
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10181
Rabphilin 3A retains NMDA receptors at synaptic sites through interaction with GluN2A/PSD-95 complex
Abstract
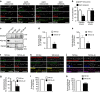
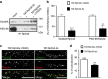
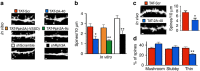
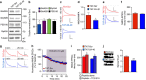
NMDA receptor (NMDAR) composition and synaptic retention represent pivotal features in the physiology and pathology of excitatory synapses. Here, we identify Rabphilin 3A (Rph3A) as a new GluN2A subunit-binding partner. Rph3A is known as a synaptic vesicle-associated protein involved in the regulation of exo- and endocytosis processes at presynaptic sites. We find that Rph3A is enriched at dendritic spines. Protein-protein interaction assays reveals that Rph3A N-terminal domain interacts with GluN2A(1349-1389) as well as with PSD-95(PDZ3) domains, creating a ternary complex. Rph3A silencing in neurons reduces the surface localization of synaptic GluN2A and NMDAR currents. Moreover, perturbing GluN2A/Rph3A interaction with interfering peptides in organotypic slices or in vivo induces a decrease of the amplitude of NMDAR-mediated currents and GluN2A density at dendritic spines. In conclusion, Rph3A interacts with GluN2A and PSD-95 forming a complex that regulates NMDARs stabilization at postsynaptic membranes.
Figures





References
-
- Papouin T. et al. Synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are gated by different endogenous coagonists. Cell 150, 633–646 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

