Tracking patterns of needs during a telephone follow-up programme for family caregivers of persons with stroke
- PMID: 26680007
- PMCID: PMC4912456
- DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1107767
Tracking patterns of needs during a telephone follow-up programme for family caregivers of persons with stroke
Abstract
Purpose: Programmes that address stroke family caregiver needs and skill-building are recommended based on the literature and patient care guidelines for stroke rehabilitation. The purpose of this study was to explore patterns of perceived needs and skill-building during a stroke caregiver intervention programme.
Method: Descriptive statistics were used to analyse data from 123 stroke caregivers enrolled in the intervention group of a randomised controlled clinical trial. Caregivers received eight weekly telephone sessions, with a booster session a month later. At each session, the Caregiver Needs and Concerns Checklist (CNCC) was used to identify and prioritise current needs that were then addressed through skill-building strategies.
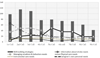
Results: Perceived needs changed over time. Information about stroke was the highest priority need during Session 1. Managing survivor emotions and behaviours was the highest priority for Sessions 2 through 4. Caregivers generally waited until Sessions 5 through 9 to address their own emotional and physical health needs. Physical and instrumental care needs were relatively low but stable across all nine sessions. Skill-building was consistently high, though it peaked during Sessions 2 and 3.
Conclusions: Tracking patterns of needs and skill-building suggest appropriate timing for targeting different types of family caregiver support during stroke rehabilitation. Implications for Rehabilitation Family caregivers of stroke survivors play an essential role in the rehabilitation process of the stroke survivor. Identifying and addressing the priority needs and concerns of stroke caregivers during the early discharge period enables caregivers to provide sustained support for the stroke survivor. Rehabilitation professionals are in a key position to address evolving caregiver needs and concerns as they transition to home settings with follow-up care.
Keywords: Behaviour; caregiver; clinical trials; family; stress; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Examining the Efficacy of the Telehealth Assessment and Skill-Building Kit (TASK III) Intervention for Stroke Caregivers: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Mar 25;14:e67219. doi: 10.2196/67219. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39937971 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a strength-oriented psychoeducation on caregiving competence, problem-solving abilities, psychosocial outcomes and physical health among family caregiver of stroke survivors: A randomised controlled trial.Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Nov;87:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 30059815 Clinical Trial.
-
Developing a complex intervention programme for informal caregivers of stroke survivors: The Caregivers' Guide.Scand J Caring Sci. 2017 Mar;31(1):146-156. doi: 10.1111/scs.12344. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Scand J Caring Sci. 2017. PMID: 27440738 Review.
-
A family caregiver-oriented discharge planning program for older stroke patients and their family caregivers.J Clin Nurs. 2008 Sep;17(18):2497-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02450.x. J Clin Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18705725 Clinical Trial.
-
"Timing It Right": a conceptual framework for addressing the support needs of family caregivers to stroke survivors from the hospital to the home.Patient Educ Couns. 2008 Mar;70(3):305-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2007.10.020. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Patient Educ Couns. 2008. PMID: 18155388 Review.
Cited by
-
Adapting the telephone assessment and skill-building kit to the telehealth technology preferences of stroke family caregivers.Res Nurs Health. 2021 Feb;44(1):81-91. doi: 10.1002/nur.22075. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Res Nurs Health. 2021. PMID: 33075163 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Efficacy of the Telehealth Assessment and Skill-Building Kit (TASK III) Intervention for Stroke Caregivers: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Mar 25;14:e67219. doi: 10.2196/67219. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39937971 Free PMC article.
-
Caregiver Tasks and Life Changes Among Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors.J Gerontol Nurs. 2025 Mar;51(3):13-18. doi: 10.3928/00989134-20250103-02. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Gerontol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39778161
-
Co-design and evaluation of a patient-centred transition programme for stroke patients, combining case management and access to an internet information platform: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial - NAVISTROKE.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Apr 22;22(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-07907-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35459183 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a patient-centered transition program for stroke survivors and their informal caregivers, combining case-management and access to an online information platform: A user-centered design approach.Digit Health. 2024 Aug 6;10:20552076241272628. doi: 10.1177/20552076241272628. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39114116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VI, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, III, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turna TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB on behalf of the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129(3):e28–3292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miller EL, Murray L, Lorie R, Zorowitz RD, Bakas T, Clark P, Billinger SA. Comprehensive overview of nursing and interdisciplinary rehabilitation care of the stroke patient: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2010;41:2402–2448. - PubMed
-
- Bakas T, Austin JK, Okonkwo KF, Lewis R, Chadwick L. Needs, concerns, strategies, and advice of stroke caregivers the first six months after discharge. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 2002;34:242–251. - PubMed
-
- Bakas T, Kroenke K, Plue LD, Perkins SM, Williams LS. Outcomes among family caregivers of aphasic versus non-aphasic stroke survivors. Rehabilitation Nursing. 2002;31:33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical