Dilated cardiomyopathy following use of xenadrine EFX
- PMID: 26680256
- PMCID: PMC5806743
- DOI: 10.1177/0394632015599701
Dilated cardiomyopathy following use of xenadrine EFX
Abstract
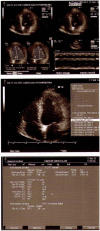
We describe a case of a 35-year-old man presented at the emergency room of our institution with acute onset of dyspnea and dizziness. He was a body builder and had been using Xenadrine EFX for weight loss reduction. The laboratory analyses were normal. A chest radiograph showed an enlarged cardiac silhouette with clear lung fields. Transtoracic two-dimensional color Doppler echocardiography revealed a diffuse hypokinesia with a marked decreased in systolic function and a high teledyastolic diameter. This case document the possible relation to use of Xenadrine EFX for weight loss and the recurrence of dilated cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: dilated cardiomyopathy; weight loss; xenadrine.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Haller CA, Benowitz NL, Jacob P., 3rd (2005) Hemodynamic effects of ephedra-free weight-loss supplements in humans. American Journal of Medicine 118: 998–1003. - PubMed
-
- Haller CA, Benowitz NL. (2000) Adverse cardiovascular and central nervous system events associated with dietary supplements containing ephedra alkaloids. New England Journal of Medicine 343:1833–1838. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan CM, Kaesberg JL, Mitchell ES, et al. (2010) Coronary artery aneurysm and thrombosis following chronic ephedra use. International Journal of Cardiology 139: 11–13. - PubMed
-
- Samenuk D, Link MS, Homoud MK, et al. (2002) Adverse cardiovascular events temporally associated with ma huang, an herbal source of ephedrine. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 77: 12–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources