Phase II trial of second-line everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RECORD-4)
- PMID: 26681676
- PMCID: PMC5006123
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdv612
Phase II trial of second-line everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RECORD-4)
Abstract
Background: RECORD-1 demonstrated clinical benefit of everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) previously treated with sunitinib, sorafenib, or both; prior treatment with cytokines, bevacizumab, and chemotherapy was also permitted. RECORD-4 prospectively assessed everolimus in a purely second-line setting.
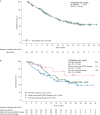
Methods: Patients with clear-cell mRCC were enrolled into one of three cohorts based on first-line therapy with sunitinib, other anti-VEGF agents, or cytokines. Patients were treated with everolimus 10 mg/day until progression (RECIST, v1.0) or intolerance. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS) per investigator review. Data cutoff was 1 September 2014, for the primary analysis and 26 June 2015, for the final overall survival (OS) analysis.
Results: Enrolled patients (N = 134) previously received sunitinib (n = 58), other anti-VEGF therapy (n = 62; sorafenib, 23; bevacizumab, 16; pazopanib, 13; tivozanib, 5; and axitinib, 3), or cytokines (n = 14). Overall median age was 59 years, and most patients were men (68%) and of favorable/intermediate MSKCC risk (52/37%). Overall median PFS was 7.8 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 5.7-11.0]; in the cohorts, it was 5.7 months (95% CI 3.7-11.3) with previous sunitinib, 7.8 months (95% CI 5.7-11.0) with other previous anti-VEGF therapy, and 12.9 months [95% CI 2.6-not estimable (NE)] with previous cytokines. Overall, 67% of patients achieved stable disease as their best objective response. At final OS analysis, total median OS was 23.8 months (95% CI 17.0-NE) and, in the cohorts, it was 23.8 months (95% CI 13.7-NE) with previous sunitinib, 17.2 months (95% CI 11.9-NE) with other previous anti-VEGF therapy, and NE (95% CI 15.9-NE) with previous cytokine-based therapy. Overall, 56% of patients experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events (regardless of relationship to study drug).
Conclusions: These results confirm the PFS benefit of second-line everolimus after first-line sunitinib or other anti-VEGF therapies. The safety profile of everolimus was consistent with previous experience.
Clinical trial name and identifier: Everolimus as Second-line Therapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (RECORD-4), ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT01491672.
Keywords: everolimus; metastatic renal cell carcinoma; prospective study; second-line; sequential targeted therapy.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Kidney Cancer (Version 3.2015). http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp(22 April 2015, date last accessed).
-
- Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S et al. . EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma. UPDATE 2014. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M et al. . Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2014; 25(suppl 3): iii49–iii56. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S et al. . Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer 2010; 116: 4256–4265. - PubMed
-
- Calvo E, Escudier B, Motzer RJ et al. . Everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: subgroup analysis of patients with 1 or 2 previous vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies enrolled in the phase III RECORD-1 study. Eur J Cancer 2012; 48: 333–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical