Optic nerve sheath diameters in healthy adults measured by computer tomography
- PMID: 26682181
- PMCID: PMC4651897
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.06.30
Optic nerve sheath diameters in healthy adults measured by computer tomography
Abstract
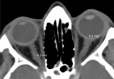
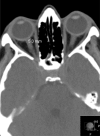
Aim: To measure optic nerve sheath diameters (ONSD) in different locations by computer tomography (CT) and to recommend the best location for cases when ONSD is used for intracranial pressure monitoring.
Methods: In a prospective cohort study, CT data of 300 healthy adults were analyzed (600 eyes). In all cases, the CT investigation was performed at the Emergency Department because of the various conditions that proved not to be connected with ophthalmological or neurological pathology. The ONSD were measured at 3 mm and 8 mm distance from the globe, and 3 mm from the anterior opening of the optic canal. The correlation analysis was performed with gender, age, and ethnic background.
Results: The right/left ONSD are 4.94±1.51/5.17±1.34 mm at 3 mm, 4.35±0.76/4.45±0.62 mm at 8 mm from the globe, and 3.55±0.82/3.65±0.7 mm at 3 mm from the optic canal. No significant differences correlated with gender of the patients, their age, and ethnic background were found.
Conclusion: In healthy persons, the ONSD varies from 5.17±1.34 mm to 3.55±0.82 mm in different locations within the intraorbital space. The most stable results with lesser standard deviation can be obtained if it is measured 8-10 mm from the globe.
Keywords: computer tomography; intracranial pressure; optic nerve sheath.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative relations between the eyeball, the optic nerve, and the optic canal important for intracranial pressure monitoring.Head Face Med. 2014 Aug 17;10:32. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-10-32. Head Face Med. 2014. PMID: 25130267 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of Intracranial Pressure by CT-Defined Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter.J Neuroimaging. 2016 May;26(3):309-14. doi: 10.1111/jon.12322. Epub 2015 Dec 21. J Neuroimaging. 2016. PMID: 26686547
-
The Measurement of Elderly Volunteers' Optic Nerve Sheath Diameters by Ocular Ultrasonography.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Jul 27;55(8):413. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080413. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31357667 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial Pressure Assessment in Traumatic Head Injury with Hemorrhage Via Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter.J Neurotrauma. 2016 Dec 1;33(23):2147-2153. doi: 10.1089/neu.2015.4293. Epub 2016 May 16. J Neurotrauma. 2016. PMID: 27048793
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter: present and future perspectives for neurologists and critical care physicians.Neurol Sci. 2019 Dec;40(12):2447-2457. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04015-x. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31367861 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring of optic sheath diameter during acute migraine attack: an objective criteria for the severity of disease.Acta Neurol Belg. 2024 Jun;124(3):865-870. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02454-0. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024. PMID: 38191866 Clinical Trial.
-
Synchronous functional magnetic resonance eye imaging, video ophthalmoscopy, and eye surface imaging reveal the human brain and eye pulsation mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 26;14(1):2250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51069-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38278832 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the retinal basis of vision across species.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Jan;21(1):5-20. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0242-1. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31780820 Review.
-
Tensile properties of glaucomatous human sclera, optic nerve, and optic nerve sheath.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024 Dec;23(6):1851-1862. doi: 10.1007/s10237-024-01872-0. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024. PMID: 39112729 Free PMC article.
-
Dilated Optic Nerve Sheath in Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Common and Not Necessarily High Intracranial Pressure.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023 Jan;44(1):91-94. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7755. Epub 2022 Dec 29. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36581456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zinn IG, Wrisberg HA. Descriptio anatomica oculi humani iconibus illustrata. Vol. 1780. Goettingae: Vandenhoeck; p. 7.
-
- Hansen HC, Helmke K. The subarachnoid space surrounding the optic nerves. An ultrasound study of the optic nerve sheath. Surg Radiol Anat. 1996;18(4):323–328. - PubMed
-
- Helmke K, Hansen HC. Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension. I. Experimental study. Pediatr Radiol. 1996;26(10):701–705. - PubMed
-
- Kimberly HH, Shah S, Marill K, Noble V. Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with direct measurement of intracranial pressure. Acad Emerg Med. 2008;15(2):201–204. - PubMed
-
- Geeraerts T, Launey Y, Martin L, Pottecher J, Vigue B, Duranteau J, Benhamou D. Ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath may be useful for detecting raised intracranial pressure after severe brain injury. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(10):1704–1711. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
