Toxic effect of NiCl2 on development of the bursa of Fabricius in broiler chickens
- PMID: 26683707
- PMCID: PMC4807987
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6591
Toxic effect of NiCl2 on development of the bursa of Fabricius in broiler chickens
Abstract
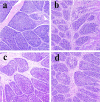
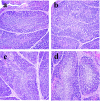
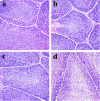
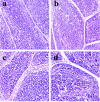
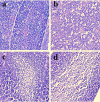
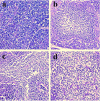
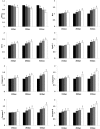
This study was conducted with objective of evaluating the toxic effects of nickel chloride (NiCl2) on development of bursa of Fabricius in broilers fed on diets supplemented with 0, 300, 600 and 900 mg/kg of NiCl2 for 42 days by using the methods of experimental pathology, flow cytometry (FCM), and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The results showed that dietary NiCl2 in 300 mg/kg and over induced toxic suppression in the bursal development, which was characterized by decreasing lymphocytes histopathologically and relative weight, increasing G0/G1 phase (a prolonged nondividing state), reducing S phase (DNA replication) and proliferating index, and increasing percentages of apoptotic cells. Concurrently, the mRNA expression levels of bax, cytochrome c (cyt c), apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 (Apaf-1), caspase-3, caspase-6, caspase-7 and caspase-9 were increased and the bcl-2 mRNA expression levels were decreased. The toxic suppression of bursal development finally impaired humoral immunity duo to the reduction of B lymphocyte population and B lymphocyte activity in the broiler chicken. This study provides new evidences for further studying the effect mechanism of Ni and Ni compoundson B-cell or bursa of Fabricius.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; NiCl2; apoptosis; cell cycle; lesion; relative weight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Scott-Fordsmand JJ. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer; 1997. Toxicity of nickel to soil organisms in Denmark; pp. 1–34.
-
- Haber LT, Erdreicht L, Diamond GL, Maier AM, Ratney R, Zhao Q. Hazard identification and dose response of inhaled nickel-soluble salts. Regul Toxicol Pharm. 2000;31:210–230. - PubMed
-
- Doreswamy K, Shrilatha B, Rajeshkumar T, Muralidhara Nickel-induced oxidative stress in testis of mice: evidence of DNA damage and genotoxic effects. J Androl. 2004;25:996–1003. - PubMed
-
- Cempel M, Nikel G. Nickel: a review of its sources and environmental toxicology. Pol J Environ Study. 2006;15:375–382.
-
- Alarifi S, Ali D, Alakhtani S, Al Suhaibani ES, Al-Qahtani AA. Reactive oxygen species-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis in human skin epidermal cells after exposure to nickel nanoparticles. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014;157:84–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

