Bromodomain and hedgehog pathway targets in small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 26683772
- PMCID: PMC4738144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.001
Bromodomain and hedgehog pathway targets in small cell lung cancer
Abstract
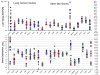
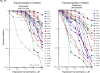
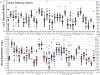
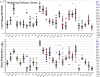
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an extremely aggressive cancer that frequently recurs. Twenty-three human SCLC lines were selected representing varied Myc status. Gene expression of lung cancer, stem-like, hedgehog pathway, and notch pathway genes were determined by RT(2)-PCR array and Exon 1.0 ST array. Etoposide and topotecan concentration response was examined. The IC50's for etoposide and topotecan ranged over nearly 3 logs upon 96 hrs exposure to the drugs. Myc status, TOP2A, TOP2B and TOP1 mRNA expression or topoisomerase 1 and topoisomerase 2 protein did not account for the range in the sensitivity to the drugs. γ-secretase inhibitors, RO429097 and PF-03084014, had little activity in the SCLC lines over ranges covering the clinical Cmax concentrations. MYC amplified lines tended to be more sensitive to the bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. The Smo antagonists, erismodegib and vismodegib and the Gli antagonists, HPI1 and SEN-450 had a trend toward greater sensitivity of the MYC amplified line. Recurrent SCLC is among the most recalcitrant cancers and drug development efforts in this cancer are a high priority.
Keywords: Bromodomain inhibitors; Hedgehog inhibitors; SCLC; SCLC gene expression; Small cell lung cancer.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures












Comment in
-
Developing New, Rational Therapies for Recalcitrant Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016 May 31;108(10):djw119. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw119. Print 2016 Oct. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016. PMID: 27247352 No abstract available.
References
-
- Paumier A, Le Pechoux C. Radiotherapy in small cell lung cancer: where should it go. Lung Cancer. 2010;69:133–40. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez E, Lilenbaum RC. Small cell lung cancer: past, present and future. Curr Oncol Rep. 2010;12:327–34. - PubMed
-
- D’Angelo SP, Pietanza MC. The molecular pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Johnson BE, Russell E, Simmons AM, Phelps R, Steinberg SM, Ihde DC, et al. MYC family DNA amplification in 126 tumor cell lines from patients with small cell lung cancer. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1996;24:210–7. - PubMed
-
- Shivapurkar N, Reddy J, Matta H, Sathyanarayana UG, Huang CX, Toyooka S, et al. Loss expression of death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) components in lung cancer cell lines and the influence of MYC amplification. Oncogene. 2002;21:8510–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

