Physical activity, smoking, and genetic predisposition to obesity in people from Pakistan: the PROMIS study
- PMID: 26683835
- PMCID: PMC4683724
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-015-0259-x
Physical activity, smoking, and genetic predisposition to obesity in people from Pakistan: the PROMIS study
Abstract
Background: Multiple genetic variants have been reliably associated with obesity-related traits in Europeans, but little is known about their associations and interactions with lifestyle factors in South Asians.
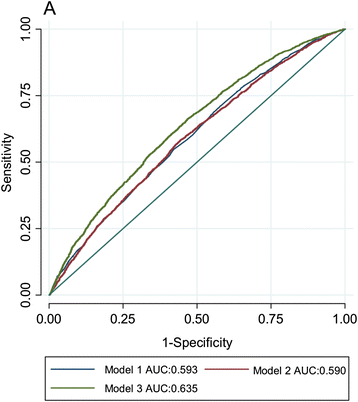
Methods: In 16,157 Pakistani adults (8232 controls; 7925 diagnosed with myocardial infarction [MI]) enrolled in the PROMIS Study, we tested whether: a) BMI-associated loci, individually or in aggregate (as a genetic risk score--GRS), are associated with BMI; b) physical activity and smoking modify the association of these loci with BMI. Analyses were adjusted for age, age(2), sex, MI (yes/no), and population substructure.
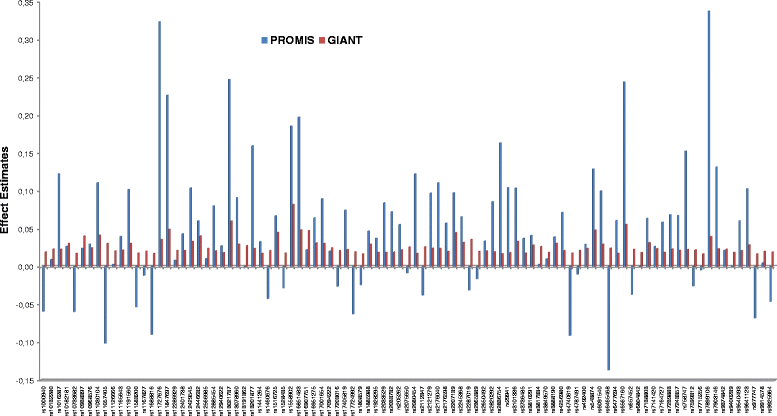
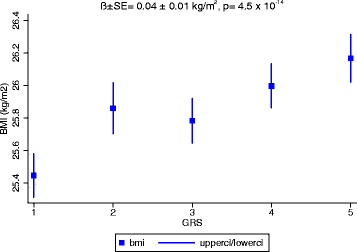
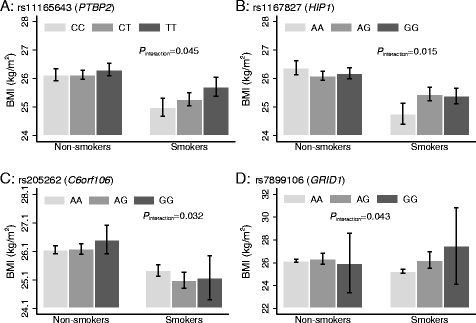
Results: Of 95 SNPs studied here, 73 showed directionally consistent effects on BMI as reported in Europeans. Each additional BMI-raising allele of the GRS was associated with 0.04 (SE = 0.01) kg/m(2) higher BMI (P = 4.5 × 10(-14)). We observed nominal evidence of interactions of CLIP1 rs11583200 (P(interaction) = 0.014), CADM2 rs13078960 (P(interaction) = 0.037) and GALNT10 rs7715256 (P(interaction) = 0.048) with physical activity, and PTBP2 rs11165643 (P(interaction) = 0.045), HIP1 rs1167827 (P(interaction) = 0.015), C6orf106 rs205262 (P(interaction) = 0.032) and GRID1 rs7899106 (P(interaction) = 0.043) with smoking on BMI.
Conclusions: Most BMI-associated loci have directionally consistent effects on BMI in Pakistanis and Europeans. There were suggestive interactions of established BMI-related SNPs with smoking or physical activity.
Figures

References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

