TREM-1-accentuated lung injury via miR-155 is inhibited by LP17 nanomedicine
- PMID: 26684249
- PMCID: PMC4773843
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00195.2015
TREM-1-accentuated lung injury via miR-155 is inhibited by LP17 nanomedicine
Abstract
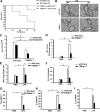
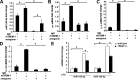
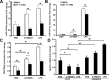
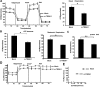
Triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cell-1 (TREM-1) is a superimmunoglobulin receptor expressed on myeloid cells. Synergy between TREM-1 and Toll-like receptor amplifies the inflammatory response; however, the mechanisms by which TREM-1 accentuates inflammation are not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the role of TREM-1 in a model of LPS-induced lung injury and neutrophilic inflammation. We show that TREM-1 is induced in lungs of mice with LPS-induced acute neutrophilic inflammation. TREM-1 knockout mice showed an improved survival after lethal doses of LPS with an attenuated inflammatory response in the lungs. Deletion of TREM-1 gene resulted in significantly reduced neutrophils and proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, particularly IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. Physiologically deletion of TREM-1 conferred an immunometabolic advantage with low oxygen consumption rate (OCR) sparing the respiratory capacity of macrophages challenged with LPS. Furthermore, we show that TREM-1 deletion results in significant attenuation of expression of miR-155 in macrophages and lungs of mice treated with LPS. Experiments with antagomir-155 confirmed that TREM-1-mediated changes were indeed dependent on miR-155 and are mediated by downregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1) a key miR-155 target. These data for the first time show that TREM-1 accentuates inflammatory response by inducing the expression of miR-155 in macrophages and suggest a novel mechanism by which TREM-1 signaling contributes to lung injury. Inhibition of TREM-1 using a nanomicellar approach resulted in ablation of neutrophilic inflammation suggesting that TREM-1 inhibition is a potential therapeutic target for neutrophilic lung inflammation and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Keywords: TREM-1; lung injury; miR-155; nanomedicine.
Figures



References
-
- Bouchon A, Dietrich J, Colonna M. Cutting edge: inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol 164: 4991–4995, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bouchon A, Facchetti F, Weigand MA, Colonna M. TREM-1 amplifies inflammation and is a crucial mediator of septic shock. Nature 410: 1103–1107, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Boufenzer A, Lemarie J, Simon T, Derive M, Bouazza Y, Tran NN, Maskali F, Groubatch F, Bonnin P, Bastien C, Bruneval P, Marie PY, Cohen R, Danchin N, Silvestre JS, Ait-Oufella H, Gibot S. TREM-1 mediates inflammatory injury and cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction. Circ Res 116: 1772–1182, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Brower RG, Ware LB, Berthiaume Y, Matthay MA. Treatment of ARDS. Chest 120: 1347–1367, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

