Central nervous system involvement by Waldenström macroglobulinaemia (Bing-Neel syndrome): a multi-institutional retrospective study
- PMID: 26686858
- PMCID: PMC5480405
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.13883
Central nervous system involvement by Waldenström macroglobulinaemia (Bing-Neel syndrome): a multi-institutional retrospective study
Abstract
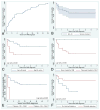
Bing-Neel syndrome (BNS) is a rare complication seen in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinaemia (WM), in which lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma cells colonize the central nervous system. In this retrospective multi-centre study, we present the clinicopathological features, imaging findings, therapy, response and outcomes of 34 patients with BNS. The median time from WM diagnosis to BNS diagnosis was 3 years, 15% of patients were diagnosed with BNS at the time of WM diagnosis, and 22% of patients developed BNS when responding to active treatment for WM. Patients with BNS presented with variable clinical features including limb motor deficits, change in mental status and cranial nerve palsies. The diagnosis was made using a combination of cerebrospinal fluid cytology, flow cytometry and detection of the MYD88 L265 mutation, and magnetic resonance imaging. The estimated 3-year overall survival rate was 59%. Of the survivors, 40% have evidence of pathological and/or radiological persistence of disease. Age older than 65 years, platelet count lower than 100 × 10(9) /l, and treatment for WM prior to BNS diagnosis were associated with worse outcome. Exposure to rituximab for treatment of BNS was associated with a better outcome. Multi-institutional collaboration is warranted to improve treatment and outcomes in patients with BNS.
Keywords: Bing-Neel syndrome; Waldenström macroglobulinaemia; central nervous system; lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JJC: Advisory Board: Gilead Sciences. Consultancy: Biogen Idec, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals. Research funding: Gilead Sciences, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics.
SD: Honoraria: Janssen.
MPL: Advisory Board: CSL Behring, Baxter Pharmaceuticals. Research funding: CSL Behring. Speaker: CSL Behring, Grifols, Kedrion. Honoraria: CSL Behring, Grifols.
MCM: Consultancy: Amgen, Celgene, Janssen Cilag.
AT: No conflict of interest to disclose.
FL: Research funding: Teva Pharmaceuticals.
MLP: No conflict of interest to disclose.
MV: No conflict of interest to disclose.
RGS: Honoraria: Novartis, Amgen, Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Research funding: Novartis. Advisory Board: Amgen.
SW: No conflict of interest to disclose.
LN: No conflict of interest to disclose.
EQL: Consultancy: Genentech.
MLR: Consultancy: N-Of-One Therapeutics.
ADN: No conflict of interest to disclose.
IMG: Advisory Board: Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Novartis, Takeda.
SPT: Research funding, consulting fees, and/or speaking honoraria from Janssen, Onyx, Pharmacyclics, Gilead Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Abdallah AO, Atrash S, Muzaffar J, Abdallah M, Kumar M, Van Rhee F, Barlogie B. Successful treatment of Bing-Neel syndrome using intrathecal chemotherapy and systemic combination chemotherapy followed by BEAM auto-transplant: a case report and review of literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013;13:502–506. - PubMed
-
- Baker WJ, Royer GL, Jr, Weiss RB. Cytarabine and neurologic toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:679–693. - PubMed
-
- Bing J, Neel A. Two cases of hyperglobulinemia with affection of the central nervous system on a toxi-infectious basis. Acta Medica Scandinavica. 1936;LXXXVIII:492–506.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

