Non-lethal Inhibition of Gut Microbial Trimethylamine Production for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 26687352
- PMCID: PMC4871610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.055
Non-lethal Inhibition of Gut Microbial Trimethylamine Production for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
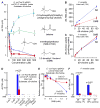
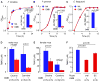
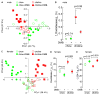
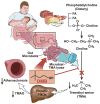
Trimethylamine (TMA) N-oxide (TMAO), a gut-microbiota-dependent metabolite, both enhances atherosclerosis in animal models and is associated with cardiovascular risks in clinical studies. Here, we investigate the impact of targeted inhibition of the first step in TMAO generation, commensal microbial TMA production, on diet-induced atherosclerosis. A structural analog of choline, 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB), is shown to non-lethally inhibit TMA formation from cultured microbes, to inhibit distinct microbial TMA lyases, and to both inhibit TMA production from physiologic polymicrobial cultures (e.g., intestinal contents, human feces) and reduce TMAO levels in mice fed a high-choline or L-carnitine diet. DMB inhibited choline diet-enhanced endogenous macrophage foam cell formation and atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein e(-/-) mice without alterations in circulating cholesterol levels. The present studies suggest that targeting gut microbial production of TMA specifically and non-lethal microbial inhibitors in general may serve as a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of cardiometabolic diseases.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Drug the Bug!Cell. 2015 Dec 17;163(7):1565-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.005. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26687345
-
Microbiome: Drugs for your bugs.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Feb;14(2):62. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.23. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26714432 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baglione J, Smith JD. Quantitative assay for mouse atherosclerosis in the aortic root. Methods in molecular medicine. 2006;129:83–95. - PubMed
-
- Bain MA, Fornasini G, Evans AM. Trimethylamine: metabolic, pharmacokinetic and safety aspects. Current drug metabolism. 2005;6:227–240. - PubMed
-
- Barlow P, Marchbanks RM. The effects of inhibiting choline dehydrogenase on choline metabolism in mice. Biochemical pharmacology. 1985;34:3117–3122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

