DNA Entry into and Exit out of the Cohesin Ring by an Interlocking Gate Mechanism
- PMID: 26687354
- PMCID: PMC4701713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.030
DNA Entry into and Exit out of the Cohesin Ring by an Interlocking Gate Mechanism
Abstract
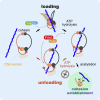
Structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC) complexes are proteinaceous rings that embrace DNA to enable vital chromosomal functions. The ring is formed by two SMC subunits, closed at a pair of ATPase heads, whose interaction is reinforced by a kleisin subunit. Using biochemical analysis of fission-yeast cohesin, we find that a similar series of events facilitates both topological entrapment and release of DNA. DNA-sensing lysines trigger ATP hydrolysis to open the SMC head interface, whereas the Wapl subunit disengages kleisin, but only after ATP rebinds. This suggests an interlocking gate mechanism for DNA transport both into and out of the cohesin ring. The entry direction is facilitated by a cohesin loader that appears to fold cohesin to expose the DNA sensor. Our results provide a model for dynamic DNA binding by all members of the SMC family and explain how lysine acetylation of cohesin establishes enduring sister chromatid cohesion.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







Comment in
-
Chromosome biology: In and out through the same cohesin door.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;17(2):66-7. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.29. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26726038 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arumugam P., Gruber S., Tanaka K., Haering C.H., Mechtler K., Nasmyth K. ATP hydrolysis is required for cohesin’s association with chromosomes. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam P., Nishino T., Haering C.H., Gruber S., Nasmyth K. Cohesin’s ATPase activity is stimulated by the C-terminal Winged-Helix domain of its kleisin subunit. Curr. Biol. 2006;16:1998–2008. - PubMed
-
- Rolef Ben-Shahar T., Heeger S., Lehane C., East P., Flynn H., Skehel M., Uhlmann F. Eco1-dependent cohesin acetylation during establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Science. 2008;321:563–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

