Pioglitazone Inhibits the Development of Hyperalgesia and Sensitization of Spinal Nociresponsive Neurons in Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 26687453
- PMCID: PMC4791042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.11.006
Pioglitazone Inhibits the Development of Hyperalgesia and Sensitization of Spinal Nociresponsive Neurons in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
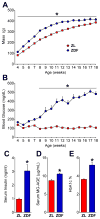
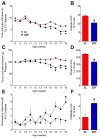
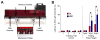
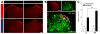
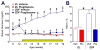
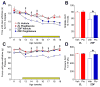
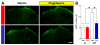
Thiazolidinedione drugs (TZDs) such as pioglitazone are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. However, whether TZDs reduce painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) remains unknown. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that chronic administration of pioglitazone would reduce PDN in Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF(fa/fa) [ZDF]) rats. Compared with Zucker Lean (ZL(fa/+)) controls, ZDF rats developed: (1) increased blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, methylglyoxal, and insulin levels; (2) mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in the hind paw; (3) increased avoidance of noxious mechanical probes in a mechanical conflict avoidance behavioral assay, to our knowledge, the first report of a measure of affective-motivational pain-like behavior in ZDF rats; and (4) exaggerated lumbar dorsal horn immunohistochemical expression of pressure-evoked phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Seven weeks of pioglitazone (30 mg/kg/d in food) reduced blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, hyperalgesia, and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase expression in ZDF. To our knowledge, this is the first report to reveal hyperalgesia and spinal sensitization in the same ZDF animals, both evoked by a noxious mechanical stimulus that reflects pressure pain frequently associated with clinical PDN. Because pioglitazone provides the combined benefit of reducing hyperglycemia, hyperalgesia, and central sensitization, we suggest that TZDs represent an attractive pharmacotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes-associated pain.
Perspective: To our knowledge, this is the first preclinical report to show that: (1) ZDF rats exhibit hyperalgesia and affective-motivational pain concurrent with central sensitization; and (2) pioglitazone reduces hyperalgesia and spinal sensitization to noxious mechanical stimulation within the same subjects. Further studies are needed to determine the anti-PDN effect of TZDs in humans.
Keywords: Zucker Diabetic Fatty rat; neuropathic pain; painful diabetic neuropathy; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Copyright © 2016 American Pain Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES:
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed N. Methylglyoxal-Derived Hydroimidazolone Advanced Glycation End-Products of Human Lens Proteins. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2003;44:5287–5292. - PubMed
-
- Aronoff S, Rosenblatt S, Braithwaite S, Egan JW, Mathisen AL, Schneider RL. Pioglitazone hydrochloride monotherapy improves glycemic control in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a 6-month randomized placebo-controlled dose-response study. The Pioglitazone 001 Study Group. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- Bierhaus A, Fleming T, Stoyanov S, Leffler A, Babes A, Neacsu C, Sauer SK, Eberhardt M, Schnolzer M, Lasitschka F, Neuhuber WL, Kichko TI, Konrade I, Elvert R, Mier W, Pirags V, Lukic IK, Morcos M, Dehmer T, Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ, Edelstein D, Nau C, Forbes J, Humpert PM, Schwaninger M, Ziegler D, Stern DM, Cooper ME, Haberkorn U, Brownlee M, Reeh PW, Nawroth PP. Methylglyoxal modification of Nav1.8 facilitates nociceptive neuron firing and causes hyperalgesia in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Med. 2012;18:926–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

