Stanene cyanide: a novel candidate of Quantum Spin Hall insulator at high temperature
- PMID: 26688269
- PMCID: PMC4685648
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18604
Stanene cyanide: a novel candidate of Quantum Spin Hall insulator at high temperature
Abstract
The search for quantum spin Hall (QSH) insulators with high stability, large and tunable gap and topological robustness, is critical for their realistic application at high temperature. Using first-principle calculations, we predict the cyanogen saturated stanene SnCN as novel topological insulators material, with a bulk gap as large as 203 meV, which can be engineered by applying biaxial strain and electric field. The band topology is identified by Z2 topological invariant together with helical edge states, and the mechanism is s-pxy band inversion at G point induced by spin-orbit coupling (SOC). Remarkably, these systems have robust topology against chemical impurities, based on the calculations on halogen and cyano group co-decorated stanene SnXxX'1-x (X,X' = F, Cl, Br, I and CN), which makes it an appropriate and flexible candidate material for spintronic devices.
Figures
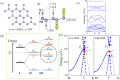
 orbitals of Sn in SnCN into conduction and valence bands at Γ point. The three stages (I–III) represent the orbital orders with atomic potential, crystal field and spin-orbit coupling taken into account sequentially. The green dashed line denotes the Fermi energy
orbitals of Sn in SnCN into conduction and valence bands at Γ point. The three stages (I–III) represent the orbital orders with atomic potential, crystal field and spin-orbit coupling taken into account sequentially. The green dashed line denotes the Fermi energy  . (e) Energy band structure near Fermi level without (left) and with (right) SOC interaction. Parities of Bloch states are denoted by +, −. The red/green dots denote s/
. (e) Energy band structure near Fermi level without (left) and with (right) SOC interaction. Parities of Bloch states are denoted by +, −. The red/green dots denote s/ dominated orbitals. The size of dot denotes the weight of projection.
dominated orbitals. The size of dot denotes the weight of projection.
 dominated orbitals. The size of dot denotes the weight of projection. (c) The energy gap as a function of extra vertical electric field. (d) Spin texture of the highest valence band of SnCN under electric field of 0.5 V/Å. Arrows refer to the in-plane orientation of spin, and the color background denotes z component of spin. (e) Spin-resolved band structure of SnCN under electric field of 0.5 V/Å. Red/blue lines denote bands with spin up/down polarization.
dominated orbitals. The size of dot denotes the weight of projection. (c) The energy gap as a function of extra vertical electric field. (d) Spin texture of the highest valence band of SnCN under electric field of 0.5 V/Å. Arrows refer to the in-plane orientation of spin, and the color background denotes z component of spin. (e) Spin-resolved band structure of SnCN under electric field of 0.5 V/Å. Red/blue lines denote bands with spin up/down polarization.
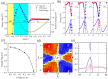
 . The evolution lines (blue dot lines) cross the arbitrary reference line (red dash line) parallel to
. The evolution lines (blue dot lines) cross the arbitrary reference line (red dash line) parallel to  an odd number of times, yielding v = 1. (c) Crystal structure for SnX0.5X′0.5 unit cell from the side view. X and X′ represent different halogeno (F, Cl, Br and I) and cyano groups. (d) The calculated enegy gap for stanene decorated by different groups.
an odd number of times, yielding v = 1. (c) Crystal structure for SnX0.5X′0.5 unit cell from the side view. X and X′ represent different halogeno (F, Cl, Br and I) and cyano groups. (d) The calculated enegy gap for stanene decorated by different groups.References
-
- Yan B. & Zhang S.-C. Topological materials. Reports on Progress in Physics 75, 096501 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Hasan M. Z. & Kane C. L. Colloquium: Topological insulators. Reviews of Modern Physics 82, 3045–3067 (2010). RMP.
-
- Qi X.-L. & Zhang S.-C. Topological insulators and superconductors. Reviews of Modern Physics 83, 1057–1110 (2011). RMP.
-
- Kane C. L. & Mele E. J. Quantum spin hall effect in graphene. Physical Review Letters 95, 226801 (2005). PRL. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H., Freimuth F., Bihlmayer G., Blügel S. & Mokrousov Y. Topological phases of bi (111) bilayer in an external exchange field. Physical Review B 86, 035104 (2012). PRB.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

