Regulatory T cell memory
- PMID: 26688349
- PMCID: PMC5113825
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2015.1
Regulatory T cell memory
Abstract
Memory for antigen is a defining feature of adaptive immunity. Antigen-specific lymphocyte populations show an increase in number and function after antigen encounter and more rapidly re-expand upon subsequent antigen exposure. Studies of immune memory have primarily focused on effector B cells and T cells with microbial specificity, using prime-challenge models of infection. However, recent work has also identified persistently expanded populations of antigen-specific regulatory T cells that protect against aberrant immune responses. In this Review, we consider the parallels between memory effector T cells and memory regulatory T cells, along with the functional implications of regulatory memory in autoimmunity, antimicrobial host defence and maternal-fetal tolerance. In addition, we discuss emerging evidence for regulatory T cell memory in humans and key unanswered questions in this rapidly evolving field.
Conflict of interest statement
statement The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
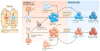

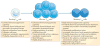
References
-
- Harty JT, Badovinac VP. Shaping and reshaping CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Homann D, Teyton L, Oldstone MB. Differential regulation of antiviral T-cell immunity results in stable CD8+ but declining CD4+ T-cell memory. Nat Med. 2001;7:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:835–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI120202/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI112186/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP2AR068130/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI110498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR066821/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR062064/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08AR062064/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1AI110498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AR068130/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI112186/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100934/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AR066821/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI100934/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI120202/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

