Optic Disc and Optic Cup Segmentation Methodologies for Glaucoma Image Detection: A Survey
- PMID: 26688751
- PMCID: PMC4673359
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/180972
Optic Disc and Optic Cup Segmentation Methodologies for Glaucoma Image Detection: A Survey
Abstract
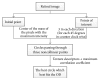
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of loss of vision in the world. Examining the head of optic nerve (cup-to-disc ratio) is very important for diagnosing glaucoma and for patient monitoring after diagnosis. Images of optic disc and optic cup are acquired by fundus camera as well as Optical Coherence Tomography. The optic disc and optic cup segmentation techniques are used to isolate the relevant parts of the retinal image and to calculate the cup-to-disc ratio. The main objective of this paper is to review segmentation methodologies and techniques for the disc and cup boundaries which are utilized to calculate the disc and cup geometrical parameters automatically and accurately to help the professionals in the glaucoma to have a wide view and more details about the optic nerve head structure using retinal fundus images. We provide a brief description of each technique, highlighting its classification and performance metrics. The current and future research directions are summarized and discussed.
Figures






































References
-
- Costagliola C., dell'Omo R., Romano M. R., Rinaldi M., Zeppa L., Parmeggiani F. Pharmacotherapy of intraocular pressure—part II. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, prostaglandin analogues and prostamides. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2009;10(17):2859–2870. doi: 10.1517/14656560903300129. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Glaucoma Society. Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma. 4th. Savona, Italy: PubliComm; 2014.
-
- Stewart W. C. Clinical Practice of Glaucoma. Thorofare, NJ, USA: SLACK Incorporated; 1990.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

