Current status of cranial stereotactic radiosurgery in the UK
- PMID: 26689091
- PMCID: PMC4985193
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20150452
Current status of cranial stereotactic radiosurgery in the UK
Abstract
Objective: To investigate and benchmark the current clinical and dosimetric practices in stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in the UK.
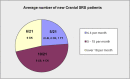
Methods: A detailed questionnaire was sent to 70 radiotherapy centres in the UK. 97% (68/70) of centres replied between June and December 2014.
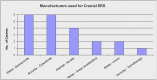
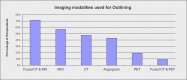
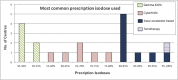
Results: 21 centres stated that they are practising SRS, and a further 12 centres plan to start SRS by the end of 2016. The most commonly treated indications are brain metastases and acoustic neuromas. A large range of prescription isodoses that range from 45% to 100% between different radiotherapy centres was seen. Ionization chambers and solid-water phantoms are used by the majority of centres for patient-specific quality assurance, and thermoplastic masks for patient immobilization are more commonly used than fixed stereotactic frames. The majority of centres perform orthogonal kilovoltage X-rays for localization before and during delivery. The acceptable setup accuracy reported ranges from 0.1 to 2 mm with a mean of 0.8 mm.
Conclusion: SRS has been increasing in use in the UK and will continue to increase in the next 2 years. There is no current consensus between SRS centres as a whole, or even between SRS centres with the same equipment, on the practices followed. This indicates the need for benchmarking and standardization in SRS practices within the UK.
Advances in knowledge: This article outlines the current practices in SRS and provides a benchmark for reference and comparison with future research in this technique.
Figures



References
-
- Sheehan JP, Yen CP, Lee CC, Loeffler JS. Cranial stereotactic radiosurgery: current status of the initial paradigm shifter. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 1–11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.53.7365. Available from: http://jco.ascopubs.org/content/32/26/2836.short - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franzini A, Marchetti M, Brait L, Milanesi I, Messina G, Forapani E, et al. . Deep brain stimulation and frameless stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of bilateral parkinsonian tremor: target selection and case report of two patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2011; 153: 1069–75. doi: 10.1007/s00701-011-0962-0. Available from: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00701-011-0962-0 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Combs SE, Thilmann C, Debus J, Schulz-Ertner D. Long-term outcome of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with acoustic neuromas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006; 64: 1341–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.10.024. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360301605028695 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Walton L, Bomford CK, Ramsden D. The Sheffield stereotactic radiosurgery unit: physical characteristics and principles of operation. Br J Radiol 1987; 60: 897–906. Available from: http://www.birpublications.org/doi/abs/10.1259/0007-1285-60-717-897 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

