First-line diagnosis of paediatric pneumonia in emergency: lung ultrasound (LUS) in addition to chest-X-ray (CXR) and its role in follow-up
- PMID: 26689098
- PMCID: PMC4985480
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20150998
First-line diagnosis of paediatric pneumonia in emergency: lung ultrasound (LUS) in addition to chest-X-ray (CXR) and its role in follow-up
Abstract
Objective: The role of lung ultrasound (LUS) integrated with chest X-ray (CXR) for the first-line diagnosis of paediatric pneumonia; to define its role during the follow-up to exclude complications.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of a cohort including 84 consecutive children (age range: 3-16 years; mean age: 6 years; 44 males, 40 females) with clinical signs of cough and fever. All the patients underwent CXR at admission integrated with LUS. Those positive at LUS were followed up with LUS until the complete resolution of the disease.
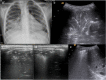
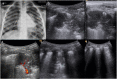
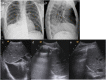
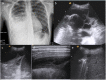
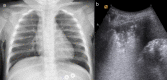
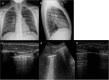
Results: CXR showed 47/84 pneumonic findings. LUS showed 60/84 pneumonic findings; 34/60 pneumonic findings had a typical pattern of lung consolidation; 26/60 pneumonic findings showed association of multiple B-lines, findings consistent with interstitial involvement, and small and hidden consolidations not achievable by CXR. One case was negative at LUS because of retroscapular location. 60 patients were followed up with LUS; 28/60 patients showed a complete regression of the disease; 23/60 patients had a significant decrease in size of consolidation; 9/60 patients showed disease stability or insignificant decrease in size, thus requiring adjunctive LUS examinations.
Conclusion: LUS, integrated with CXR, revealed to be an accurate first-line technique to identify small pneumonic consolidations, especially for "CXR-occult" findings, and for early diagnosis of pleural effusion; furthermore, LUS follow-up allows complications to be verified and additional radiation exposures to be avoided.
Advances in knowledge: The effective role of LUS in the diagnosis and follow-up of lung consolidations and pleural effusions in paediatric patients in an emergency setting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung ultrasound characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013 Mar;48(3):280-7. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22585. Epub 2012 May 2. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013. PMID: 22553150 Clinical Trial.
-
Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and monitoring of community acquired pneumonia in children.Respir Med. 2015 Sep;109(9):1207-12. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26138897
-
Lung Ultrasonography: A Viable Alternative to Chest Radiography in Children with Suspected Pneumonia?J Pediatr. 2016 Sep;176:93-98.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.05.033. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27318374
-
Lung ultrasound in community-acquired pneumonia and in interstitial lung diseases.Respiration. 2014;87(3):179-89. doi: 10.1159/000357449. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Respiration. 2014. PMID: 24481027 Review.
-
The utility of chest x-ray and lung ultrasound in the management of infants and children presenting with severe pneumonia in low-and middle-income countries: A pragmatic scoping review.J Glob Health. 2022 Dec 23;12:10013. doi: 10.7189/jogh.12.10013. J Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 36560909 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extended-FAST plus MDCT in pneumothorax diagnosis of major trauma: time to revisit ATLS imaging approach?J Ultrasound. 2019 Dec;22(4):461-469. doi: 10.1007/s40477-019-00410-4. Epub 2019 Nov 4. J Ultrasound. 2019. PMID: 31686355 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of COVID-19 Pandemic in Paediatric Age Group: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Virol. 2020 Jul;128:104395. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104395. Epub 2020 May 8. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32417675 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographic diagnosis of pneumonia: it is time to change.Br J Radiol. 2017 Jan;90(1069):20160799. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160799. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Br J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 27826986 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Point-of-care ultrasound by the pediatrician in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2021 Jan-Feb;97(1):13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Aug 9. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2021. PMID: 32781037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiological diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a Practical Guide.Acta Biomed. 2020 Jul 13;91(8-S):51-59. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i8-S.9973. Acta Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32945279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

