Narrative overview of animal and human brucellosis in Morocco: intensification of livestock production as a driver for emergence?
- PMID: 26690090
- PMCID: PMC4687311
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-015-0086-5
Narrative overview of animal and human brucellosis in Morocco: intensification of livestock production as a driver for emergence?
Abstract
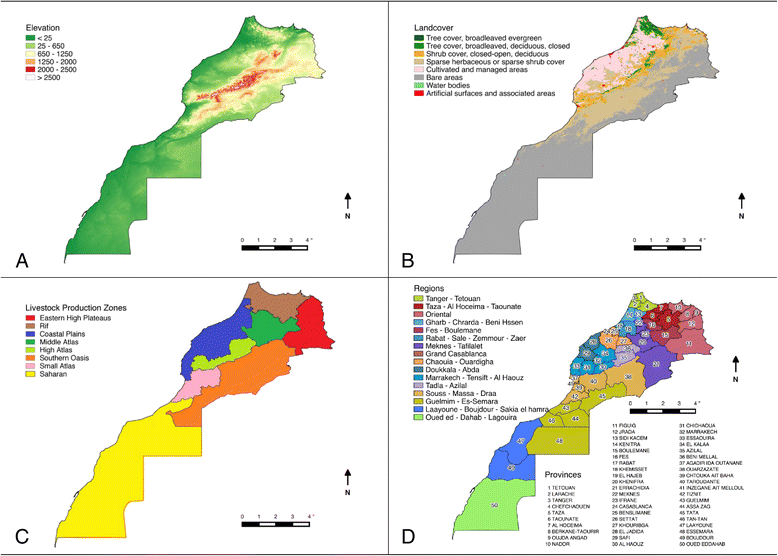
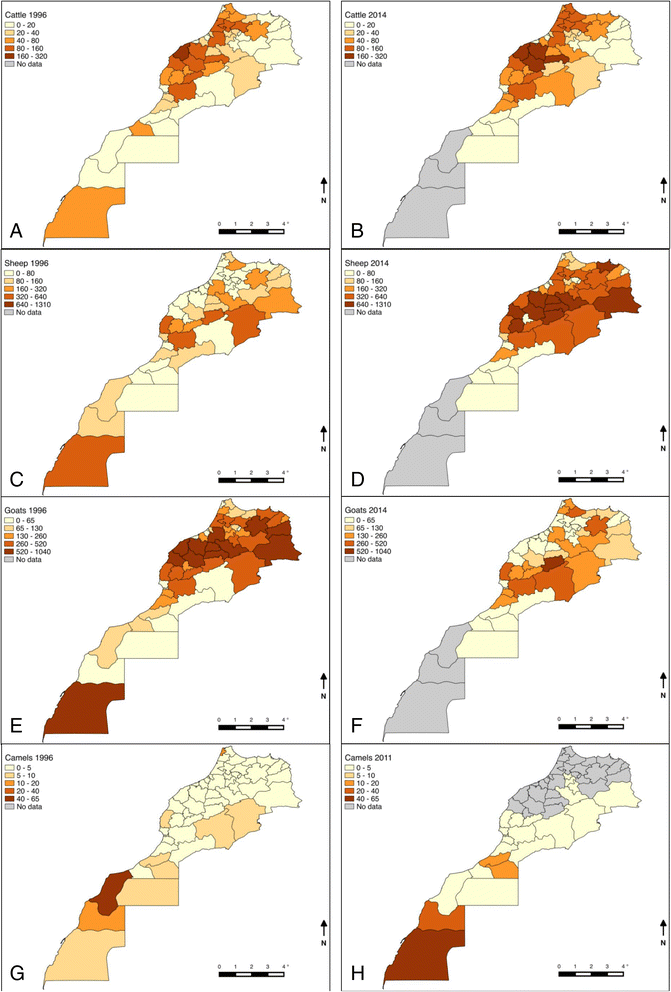
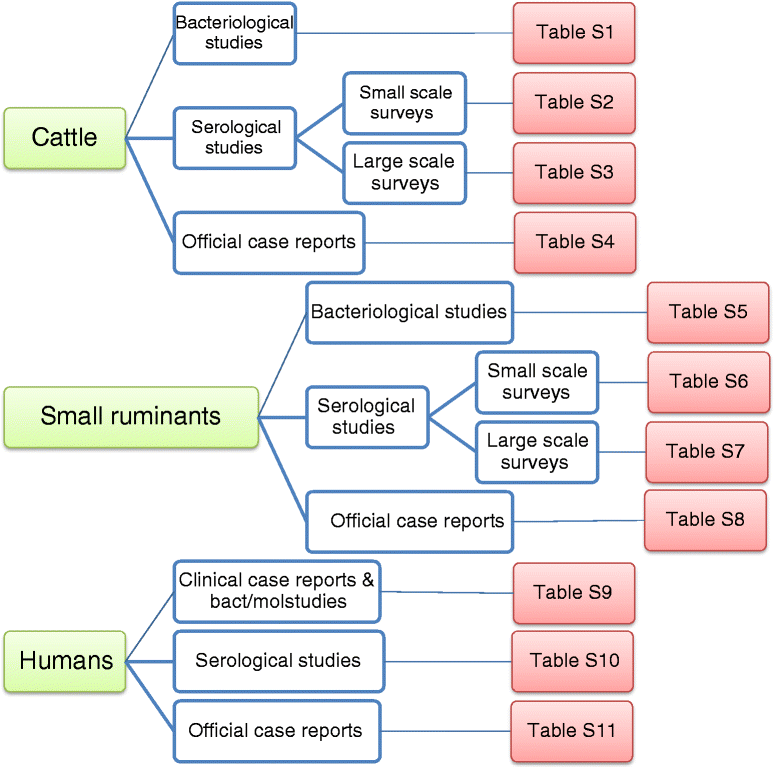
Brucellosis is one of the most widespread zoonoses in the world caused by several species of the genus Brucella. The disease, eradicated in many developed countries, is a re-emerging neglected zoonosis endemic in several zones especially in the Mediterranean region, impacting on human health and livestock production. A One Health approach could address brucellosis control in Morocco but scarcity of reliable epidemiological data, as well as underreporting, hinders the implementation of sustainable control strategies. Surveillance and control policies implemented by the Moroccan government in domestic animals (cattle and small ruminants) in the last few decades are assessed for disease impact. This study considers the origins of animal brucellosis in Morocco and the potential for emergence of brucellosis during a shift from extensive to intensive livestock production.
Figures
References
-
- McDermott J, Grace D, Zinsstag J. Economics of brucellosis impact and control in low-income countries. Rev Sci Tech. 2013;32(1):249–261. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Brucellosis in humans and animals: WHO guidance. Geneva, World Health Organization. In: Heymann DL, editor. Control of communicable diseases manual: an official report of the American Public Health Association. 18. Washington DC: World Health Organization/American Public Health Association; 2005.
-
- FAO . Guidelines for coordinated human and animal brucellosis surveillance. Rome: Animal Production and Health Division FAO Agriculture Department; 2003.
-
- LPSN bacterio.net. List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. http://www.bacterio.net/-allnamesac.html. Accessed 23 October 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

