Pharmaceutical Potential of Synthetic and Natural Pyrrolomycins
- PMID: 26690095
- PMCID: PMC6331927
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules201219797
Pharmaceutical Potential of Synthetic and Natural Pyrrolomycins
Abstract
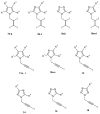
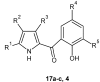
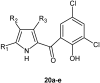
The emergence of antibiotic resistance is currently considered one of the most important global health problem. The continuous onset of multidrug-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains limits the clinical efficacy of most of the marketed antibiotics. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new antibiotics. Pyrrolomycins are a class of biologically active compounds that exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities, including antibacterial, antifungal, anthelmintic, antiproliferative, insecticidal, and acaricidal activities. In this review we focus on the antibacterial activity and antibiofilm activity of pyrrolomycins against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. Their efficacy, combined in some cases with a low toxicity, confers to these molecules a great potential for the development of new antimicrobial agents to face the antibiotic crisis.
Keywords: antibiofilm agents; antibiotic resistance; pentabromopseudilin; pyoluteorin; pyrrolomycins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers of Diseases Control and Prevention. [(accessed on 2 December 2015)]; Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf.
-
- Cascioferro S., Schillaci D. The Future of Antibiotic: From the Magic Bullet to the Smart Bullet. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2014;6:e118. doi: 10.4172/1948-5948.1000e118. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

