The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 26690110
- PMCID: PMC6331908
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules201219826
The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
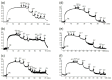
Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaf is a traditional Chinese antihypertensive and antidiabetic medicine. We examined the effects of chronic Eucommia leaf extract (ELE) administration on artery function and morphology in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). ELE was orally administered via normal diet ad libitum to six-week-old male SHRs at a concentration of 5% for seven weeks. Acetylcholine (ACh)-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation, sodium nitroprusside (SNP)-induced endothelium-independent relaxation, plasma nitric oxide (NO) levels, and media thickness were assessed. ELE significantly improved ACh-induced aortic endothelium-dependent relaxation but did not affect SNP-induced endothelium-independent relaxation in the SHRs, as compared to the animals receiving normal diet. Plasma NO levels and media thickness were significantly increased and decreased, respectively, in the ELE-treated SHRs. Therefore, long-term ELE administration may effectively improve vascular function by increasing plasma NO levels and bioavailability, and by preventing vascular hypertrophy in the SHR aorta.
Keywords: ACh-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation; Eucommia leaf extract; aortic media thickness; nitric oxide; spontaneously hypertensive rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization . A Global Brief on Hypertension-Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. WHO Reference Number: WHO/DCO/WHD/2013.2.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

