Possible Mechanisms of Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate-Induced MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression in A7r5 Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 26690114
- PMCID: PMC4691078
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms161226131
Possible Mechanisms of Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate-Induced MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression in A7r5 Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
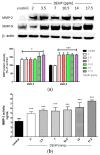
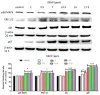
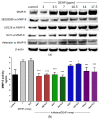
Proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) are important in the development and/or progression of many cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis. Evidence shows that matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 are related to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in atherosclerosis are regulated via various pathways, such as p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), Akt, and nuclear factor kappa (NF-κB). Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) has been shown to induce atherosclerosis by increasing tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) productions. However, whether DEHP poses any effects on MMP-2 or MMP-9 expression in VSMC has not yet been answered. In our studies, rat aorta VSMC was treated with DEHP (between 2 and 17.5 ppm) and p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, Akt, NF-κB, and MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins and activities were measured. Results showed that the presence of DEHP can induce higher MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression than the controls. Similar results on MMP-regulating proteins, i.e., p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, Akt, and NF-κB, were also observed. In summary, our current results have showed that DEHP can be a potent inducer of atherosclerosis by increasing MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression at least through the regulations of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, Akt, and NF-κB.
Keywords: Akt; ERK1/2; MMP-2; MMP-9; NF-κB; di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP); p38 MAPK; vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC).
Figures





References
-
- Rudijanto A. The role of vascular smooth muscle cells on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Acta Med. Indones. 2007;39:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Shah P.K., Galis Z.S. Matrix metalloproteinase hypothesis of plaque rupture: Players keep piling up but questions remain. Circulation. 2001;104:1878–1880. - PubMed
-
- Risinger G.M., Jr., Hunt T.S., Updike D.L., Bullen E.C., Howard E.W. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by both stimulatory and inhibitory signals in response to growth factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:25915–25925. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513513200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

