The Safety Evaluation of Salvianolic Acid B and Ginsenoside Rg1 Combination on Mice
- PMID: 26690140
- PMCID: PMC4691119
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms161226176
The Safety Evaluation of Salvianolic Acid B and Ginsenoside Rg1 Combination on Mice
Abstract
Our previous study indicated that the combination of salvianolic acid B (SalB) and ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1), the main components of Salvia miltiorrhizae and Panax notoginseng, improves myocardium structure and ventricular function in rats with ischemia/reperfusion injury. The present study aimed to determine the safety of the combined SalB and Rg1 (SalB-Rg1) in mice. The safety of SalB-Rg1 was evaluated through acute toxicity and repeated-dose toxicity. In the acute toxicity study, the up and down procedure was carried out firstly, and then, the Bliss method was applied. In the toxicity study for seven-day repeated treatment of SalB-Rg1, forty Kunming mice were randomly divided into four groups. The intravenous median lethal dose (LD50) of the SalB-Rg1 combination was 1747 mg/kg using the Bliss method. For both the acute toxicity study and the seven-day repeated toxicity study, SalB-Rg1 did not induce significant abnormality on brain, heart, kidney, liver and lung structure at any dose based on H&E stain. There were no significant changes related to the SalB-Rg1 toxicity detected on biochemical parameters for two kinds of toxicity studies. The LD50 in mice was 1747 mg/kg, which was more than one hundred times higher than the effective dose. Both studies of acute toxicity and seven-day repeated dose toxicity indicated the safety of the SalB-Rg1 combination.
Keywords: acute toxicity; ginsenoside Rg1; repeated toxicity; safety; salvianolic acid B.
Figures
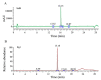



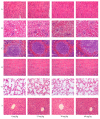
References
-
- Chun-Sheng L., Hsiao-Meng Y., Yun-Hsiang H., Chun P., Chi-Fen S. Radix salviae miltiorrhizae and Rhizoma ligustici wallichii in coronary heart disease. Chin. Med. J. 1978;4:43–46. - PubMed
-
- Yang T.Y., Wei J.C., Lee M.Y., Chen C.M., Ueng K.C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of Fufang Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) as add-on antihypertensive therapy in Taiwanese patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Phytother. Res. 2012;26:291–298. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3548. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

